DrawPPplot¶
(Source code, png)
- DrawPPplot(*args)¶
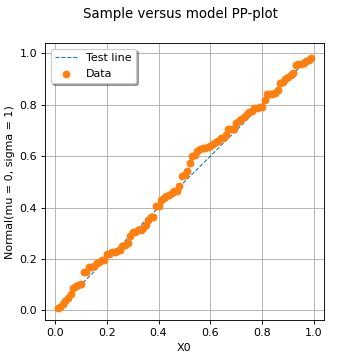
Draw a PP-plot.
- Available usages:
VisualTest.DrawPPplot(sample1, sample2, n_points)
VisualTest.DrawPPplot(sample1, distribution);
- Parameters:
- sample1, sample22-d sequences of float
Tested samples.
- ditribution
Distribution Tested model.
- n_pointsint, optional
The number of points that is used for interpolating the empirical CDF of the two samples (with possibly different sizes).
It will default to DistributionImplementation-DefaultPointNumber from the
ResourceMap.
- Returns:
- graph
Graph The graph object
- graph
Notes
The PP-plot is a visual fitting test for univariate distributions. It opposes the sample quantiles to those of the tested quantity (either a distribution or another sample) by plotting the following points cloud:
where
denotes the empirical CDF of the (first) tested sample.
If the given sample fits the tested distribution or sample, then the points should be almost aligned (up to the uncertainty associated with the estimation of the empirical probabilities) with the first bisector whose equation is:
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> from openturns.viewer import View
Generate a random sample from a Normal distribution:
>>> ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0) >>> distribution = ot.WeibullMin(2.0, 0.5) >>> sample = distribution.getSample(30) >>> sample.setDescription(['Sample'])
Draw a PP-plot against a given (inferred) distribution:
>>> tested_distribution = ot.WeibullMinFactory().build(sample) >>> graph = ot.VisualTest.DrawQQplot(sample, tested_distribution) >>> View(graph).show()
Draw a two-sample PP-plot:
>>> another_sample = distribution.getSample(50) >>> another_sample.setDescription(['Another sample']) >>> graph = ot.VisualTest.DrawQQplot(sample, another_sample) >>> View(graph).show()
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS