Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Calibration of the flooding model¶
In this example we are interested in the calibration of the flooding model. In this example we calibrate the parameters of a flooding model where only the difference between the downstream and upstream riverbed levels can be calibrated. This example shows how to manage the lack of identifiability in a calibration problem.
Parameters to calibrate¶
The vector of parameters to calibrate is:
The variables to calibrate are and are set to the following values:
Observations¶
In this section, we describe the statistical model associated with the observations.
The errors of the water heights are associated with a normal distribution with a zero mean and a standard variation equal to:
Therefore, the observed water heights are:
for where
and we make the hypothesis that the observation errors are independent. We consider a sample size equal to:
The observations are the couples , i.e. each observation is a couple made of the flowrate and the corresponding river height.
Variables¶
Q : Input. Observed.
Ks, Zv, Zm : Input. Calibrated.
H: Output. Observed.
Analysis¶
In the description of the flooding model, we see that only one parameter can be identified. Hence, calibrating this model requires some regularization. We return to this topic when analyzing the singular values of the Jacobian matrix.
Generate the observations¶
from openturns.usecases import flood_model
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
import openturns.viewer as viewer
import numpy as np
import openturns as ot
ot.ResourceMap.SetAsUnsignedInteger("Normal-SmallDimension", 1)
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
We load the flooding use case :
fm = flood_model.FloodModel()
We define the model which has 4 inputs and one output H.
The nonlinear least squares does not take into account for bounds in the parameters. Therefore, we ensure that the output is computed whatever the inputs. The model fails into two situations:
if
,
if
.
In these cases, we return an infinite number, so that the optimization algorithm does not get trapped.
def functionFlooding(X):
L = 5.0e3
B = 300.0
Q, K_s, Z_v, Z_m = X
alpha = (Z_m - Z_v) / L
if alpha < 0.0 or K_s <= 0.0:
H = np.inf
else:
H = (Q / (K_s * B * np.sqrt(alpha))) ** (3.0 / 5.0)
return [H]
g = ot.PythonFunction(4, 1, functionFlooding)
g = ot.MemoizeFunction(g)
g.setOutputDescription(["H (m)"])
We load the input distribution for :
Q = fm.Q
print(Q)
TruncatedDistribution(Gumbel(beta = 558, gamma = 1013), bounds = [0, (19000.8) +inf[)
Set the parameters to be calibrated.
K_s = ot.Dirac(30.0)
Z_v = ot.Dirac(50.0)
Z_m = ot.Dirac(55.0)
K_s.setDescription(["Ks (m^(1/3)/s)"])
Z_v.setDescription(["Zv (m)"])
Z_m.setDescription(["Zm (m)"])
Create the joint input distribution.
inputRandomVector = ot.ComposedDistribution([Q, K_s, Z_v, Z_m])
Create a Monte-Carlo sample of the output H.
nbobs = 100
inputSample = inputRandomVector.getSample(nbobs)
outputH = g(inputSample)
Observe the distribution of the output H.
graph = ot.HistogramFactory().build(outputH).drawPDF()
view = viewer.View(graph)
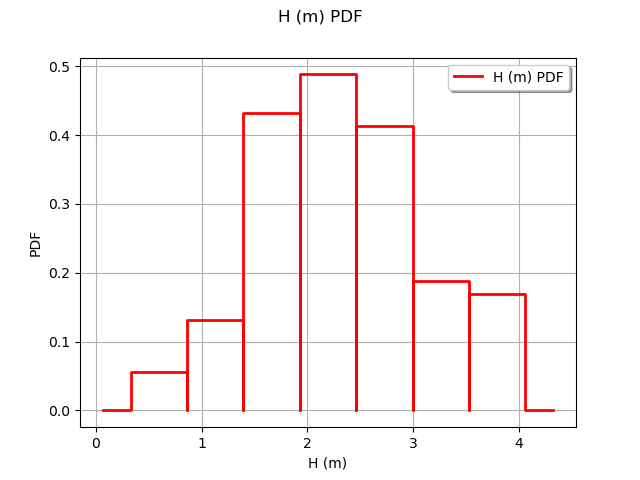
Generate the observation noise and add it to the output of the model.
sigmaObservationNoiseH = 0.1 # (m)
noiseH = ot.Normal(0.0, sigmaObservationNoiseH)
sampleNoiseH = noiseH.getSample(nbobs)
Hobs = outputH + sampleNoiseH
Plot the Y observations versus the X observations.
Qobs = inputSample[:, 0]
graph = ot.Graph("Observations", "Q (m3/s)", "H (m)", True)
cloud = ot.Cloud(Qobs, Hobs)
graph.add(cloud)
view = viewer.View(graph)
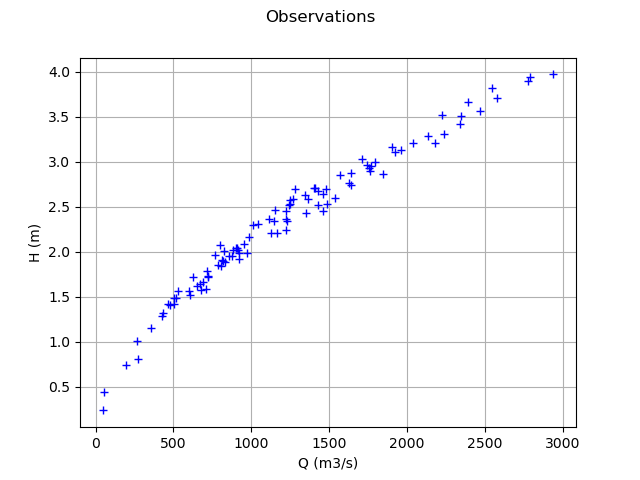
Setting the calibration parameters¶
Define the value of the reference values of the parameter. In the bayesian framework, this is called the mean of the prior normal distribution. In the data assimilation framework, this is called the background.
KsInitial = 20.0
ZvInitial = 49.0
ZmInitial = 51.0
thetaPrior = [KsInitial, ZvInitial, ZmInitial]
The following statement create the calibrated function from the model. The calibrated parameters ,
,
are at indices 1, 2, 3 in the inputs arguments of the model.
calibratedIndices = [1, 2, 3]
mycf = ot.ParametricFunction(g, calibratedIndices, thetaPrior)
Calibration with linear least squares¶
The LinearLeastSquaresCalibration class performs the linear least squares calibration by linearizing the model in the neighbourhood of the reference point.
algo = ot.LinearLeastSquaresCalibration(mycf, Qobs, Hobs, thetaPrior, "SVD")
The run method computes the solution of the problem.
algo.run()
calibrationResult = algo.getResult()
The getParameterMAP method returns the maximum of the posterior distribution of .
thetaStar = calibrationResult.getParameterMAP()
print(thetaStar)
[6.40917e+08,-5.40724e+23,-5.40724e+23]
In this case, we see that there seems to be a great distance from the reference value of to the optimum: the values seem too large in magnitude. The value of the optimum
is nonpositive. In fact, there is an identification problem because the Jacobian matrix is rank-degenerate.
Diagnostic of the identification issue¶
In this section, we show how to diagnose the identification problem.
The getParameterPosterior method returns the posterior normal distribution of .
distributionPosterior = calibrationResult.getParameterPosterior()
print(distributionPosterior)
Normal(mu = [6.40917e+08,-5.40724e+23,-5.40724e+23], sigma = [2.20186e+26,1.731e+32,1.731e+32], R = [[ 1 2.5654e-25 -2.5654e-25 ]
[ 2.5654e-25 1 1 ]
[ -2.5654e-25 1 1 ]])
We see that there is a large covariance matrix diagonal.
Let us compute a 95% confidence interval for the solution .
print(
distributionPosterior.computeBilateralConfidenceIntervalWithMarginalProbability(
0.95
)[0]
)
[-4.92304e+26, 4.92304e+26]
[-3.87025e+32, 3.87025e+32]
[-3.87025e+32, 3.87025e+32]
The confidence interval is very large. In order to clarify the situation, we compute the Jacobian matrix of the model at the candidate point.
mycf.setParameter(thetaPrior)
thetaDim = len(thetaPrior)
jacobianMatrix = ot.Matrix(nbobs, thetaDim)
for i in range(nbobs):
jacobianMatrix[i, :] = mycf.parameterGradient(Qobs[i]).transpose()
print(jacobianMatrix[0:5, :])
5x3
[[ -0.0191253 0.0956267 -0.0956267 ]
[ -0.122262 0.611308 -0.611308 ]
[ -0.144199 0.720994 -0.720994 ]
[ -0.100716 0.50358 -0.50358 ]
[ -0.0945721 0.47286 -0.47286 ]]
The rank of the problem can be seen from the singular values of the Jacobian matrix.
print(jacobianMatrix.computeSingularValues())
[8.83119,1.44233e-10,1.8607e-25]
We can see that there are two singular values which are relatively close to zero.
This explains why the Jacobian matrix is close to being rank-degenerate.
Moreover, this allows one to compute the actual dimensionality of the problem.
The algorithm we use computes the singular values in descending order.
Moreover, by definition, the singular values are nonnegative.
We see that the first singular value is close to
and the others are very close to
in comparison.
This implies that the (numerical) rank of the Jacobian matrix is 1,
even if there are 3 parameters.
Hence, only one parameter can be identified, be it ,
or
.
The choice of the particular parameter to identify is free.
However, in hydraulic studies, the parameter
is classically
calibrated while
and
are left constant.
Conclusion of the linear least squares calibration¶
There are several methods to solve the problem.
Given that the problem is not identifiable, we can use some regularization method. Two methods are provided in the library: the Gaussian linear least squares GaussianLinearCalibration and the Gaussian non linear least squares GaussianNonlinearCalibration.
We can change the problem, replacing it with a problem which is identifiable. In the flooding model, we can view
and
as constants and calibrate
only.
Calibration with non linear least squares¶
The NonLinearLeastSquaresCalibration class performs the non linear least squares calibration by minimizing the squared euclidian norm between the predictions and the observations.
algo = ot.NonLinearLeastSquaresCalibration(mycf, Qobs, Hobs, thetaPrior)
The run method computes the solution of the problem.
algo.run()
calibrationResult = algo.getResult()
Analysis of the results¶
The getParameterMAP method returns the maximum of the posterior distribution of .
thetaMAP = calibrationResult.getParameterMAP()
print(thetaMAP)
[27.7124,47.0447,52.9553]
We can compute a 95% confidence interval of the parameter .
This confidence interval is based on bootstrap, based on a sample size equal to 100 (as long as the value of the ResourceMap key “NonLinearLeastSquaresCalibration-BootstrapSize” is unchanged). This confidence interval reflects the sensitivity of the optimum to the variability in the observations.
thetaPosterior = calibrationResult.getParameterPosterior()
print(thetaPosterior.computeBilateralConfidenceIntervalWithMarginalProbability(0.95)[0])
[27.5626, 27.8524]
[46.9849, 47.1086]
[52.8914, 53.0151]
In this case, the value of the parameter is quite accurately computed, but there is a relatively large uncertainty on the values of
and
.
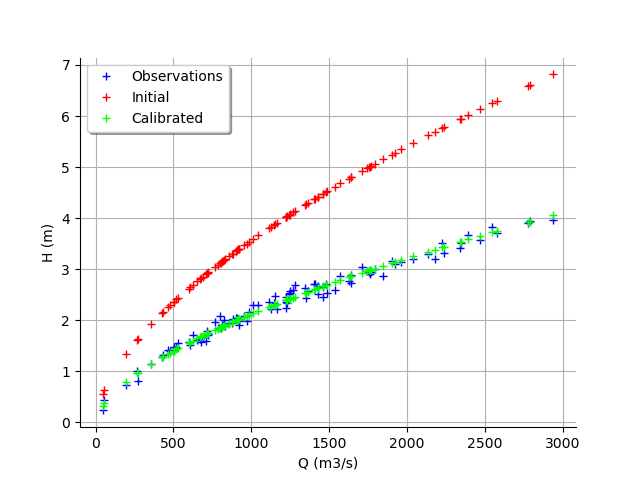
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsInputs()
graph.setLegendPosition("topleft")
view = viewer.View(graph)
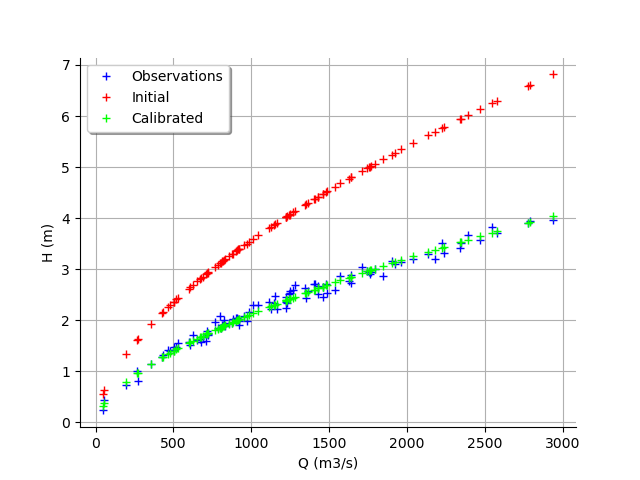
We see that there is a good fit after calibration, since the predictions after calibration (i.e. the green crosses) are close to the observations (i.e. the blue crosses).
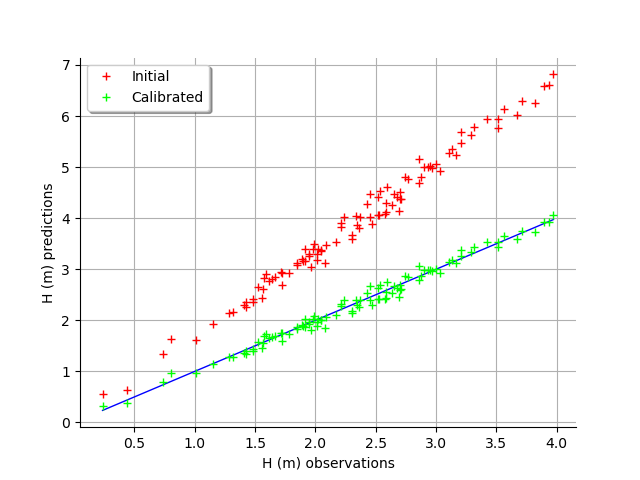
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsPredictions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
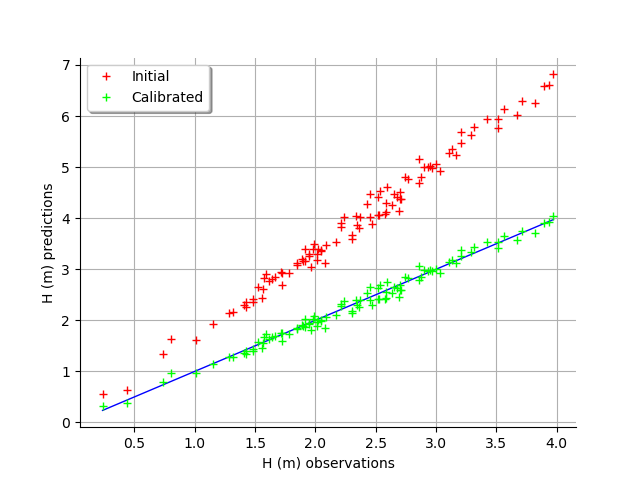
We see that there is a much better fit after calibration, since the predictions are close to the diagonal of the graphics.
observationError = calibrationResult.getObservationsError()
print(observationError)
Normal(mu = -0.00458739, sigma = 0.0922988)
We can see that the observation error is close to have a zero mean and a standard deviation equal to 0.1.
graph = calibrationResult.drawResiduals()
graph.setLegendPosition("topleft")
view = viewer.View(graph)
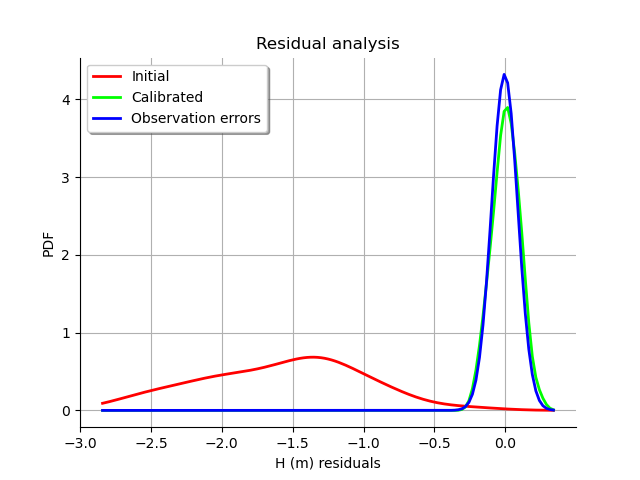
The analysis of the residuals shows that the distribution is centered on zero and symmetric. This indicates that the calibration performed well.
Moreover, the distribution of the residuals is close to being Gaussian.
graph = calibrationResult.drawParameterDistributions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
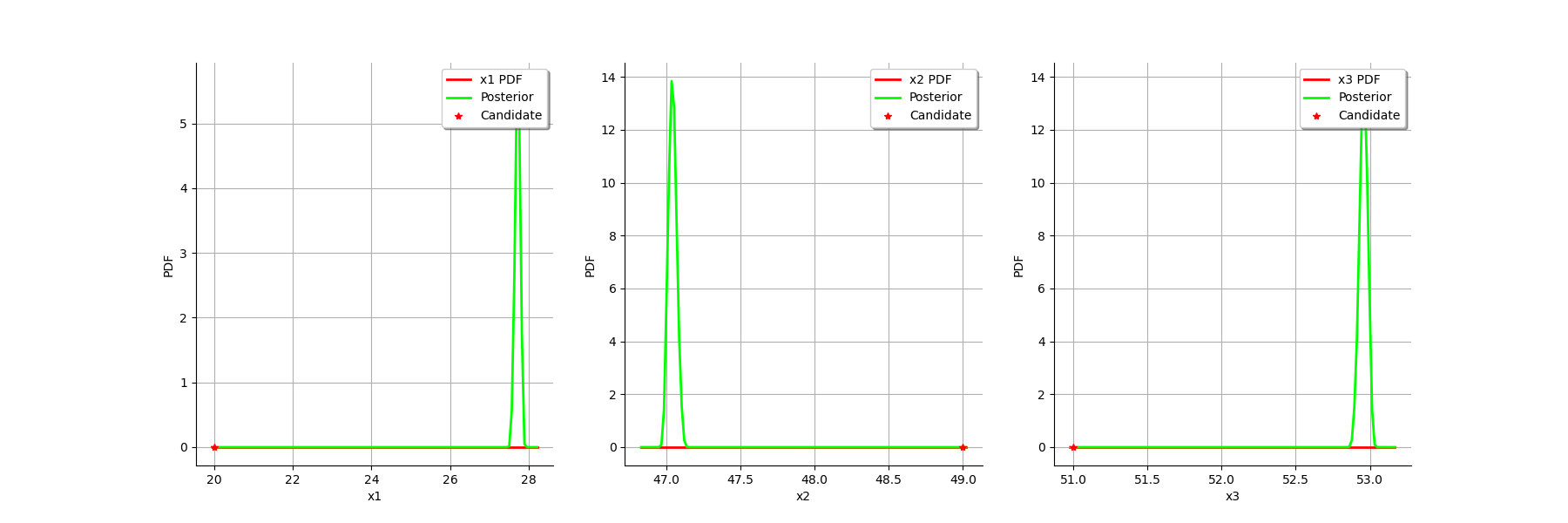
Gaussian linear calibration¶
The standard deviation of the observations.
sigmaH = 0.5 # (m^2)
Define the covariance matrix of the output Y of the model.
errorCovariance = ot.CovarianceMatrix(1)
errorCovariance[0, 0] = sigmaH**2
Define the covariance matrix of the parameters to calibrate.
sigmaKs = 5.0
sigmaZv = 1.0
sigmaZm = 1.0
sigma = ot.CovarianceMatrix(3)
sigma[0, 0] = sigmaKs**2
sigma[1, 1] = sigmaZv**2
sigma[2, 2] = sigmaZm**2
print(sigma)
[[ 25 0 0 ]
[ 0 1 0 ]
[ 0 0 1 ]]
The GaussianLinearCalibration class performs Gaussian linear calibration by linearizing the model in the neighbourhood of the prior.
algo = ot.GaussianLinearCalibration(
mycf, Qobs, Hobs, thetaPrior, sigma, errorCovariance, "SVD"
)
The run method computes the solution of the problem.
algo.run()
calibrationResult = algo.getResult()
Analysis of the results¶
The getParameterMAP method returns the maximum of the posterior distribution of .
thetaStar = calibrationResult.getParameterMAP()
print(thetaStar)
[24.5007,48.0999,51.9001]
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsInputs()
graph.setLegendPosition("topleft")
view = viewer.View(graph)
We see that the output of the model after calibration is closer to the observations. However, there is still a distance from the outputs of the model to the observations. This indicates that the calibration cannot be performed with this method.
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsPredictions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
In this case, the fit is better after calibration, but not perfect. Indeed, the cloud of points after calibration is not centered on the diagonal.
graph = calibrationResult.drawResiduals()
graph.setLegendPosition("topleft")
view = viewer.View(graph)
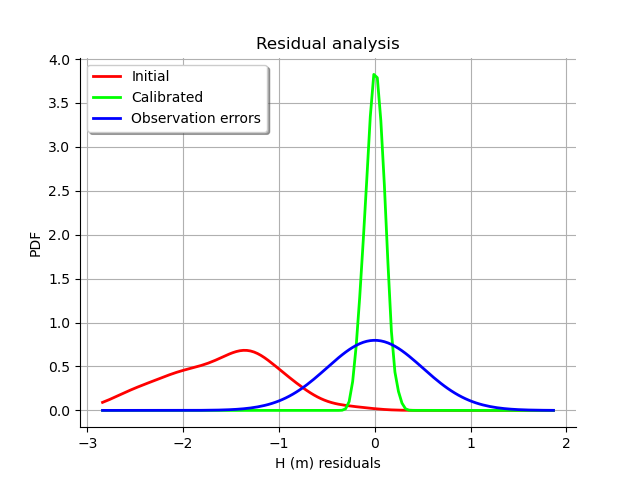
We see that the distribution of the residual is not centered on zero: the mean residual is approximately , which implies that the predictions are, on average, smaller than the observations. This is a proof that the calibration cannot be performed with this method in this particular case.
The getParameterPosterior method returns the posterior normal distribution of .
distributionPosterior = calibrationResult.getParameterPosterior()
print(distributionPosterior)
Normal(mu = [24.5007,48.0999,51.9001], sigma = [4.0847,0.81694,0.81694], R = [[ 1 0.49837 -0.49837 ]
[ 0.49837 1 0.498371 ]
[ -0.49837 0.498371 1 ]])
We can compute a 95% confidence interval of the parameter .
print(
distributionPosterior.computeBilateralConfidenceIntervalWithMarginalProbability(
0.95
)[0]
)
[14.9237, 34.0776]
[46.1845, 50.0153]
[49.9847, 53.8155]
We see that there is a large uncertainty on the value of the parameter which can be as small as
and as large as
.
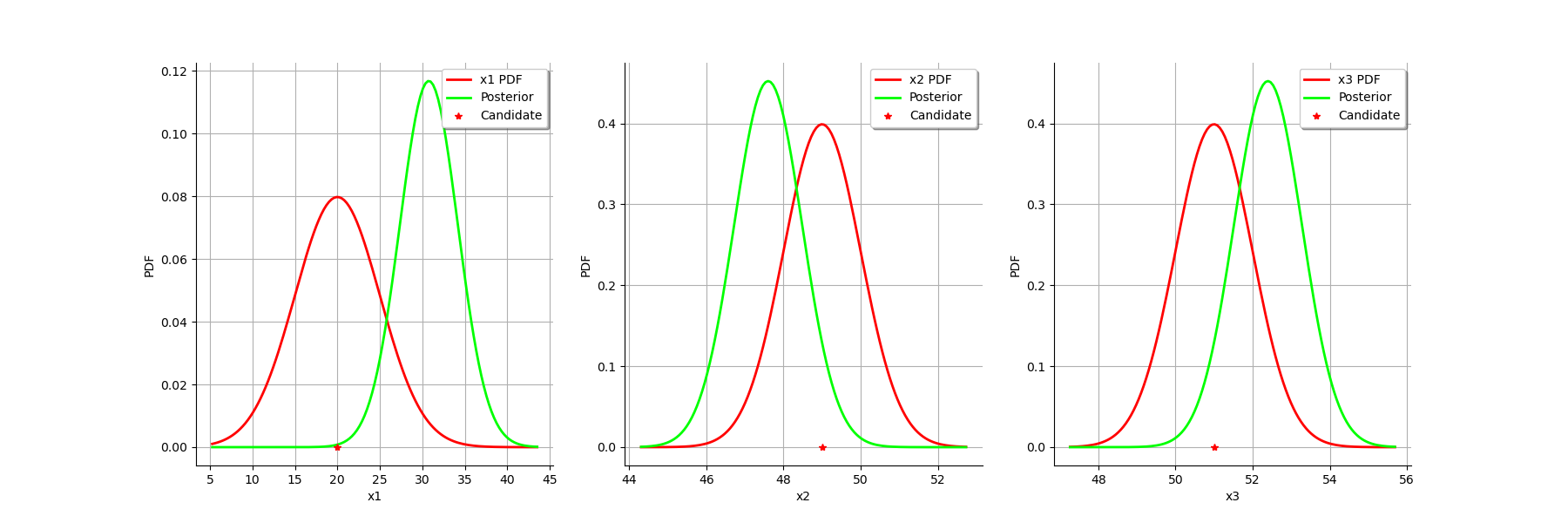
We can compare the prior and posterior distributions of the marginals of .
graph = calibrationResult.drawParameterDistributions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
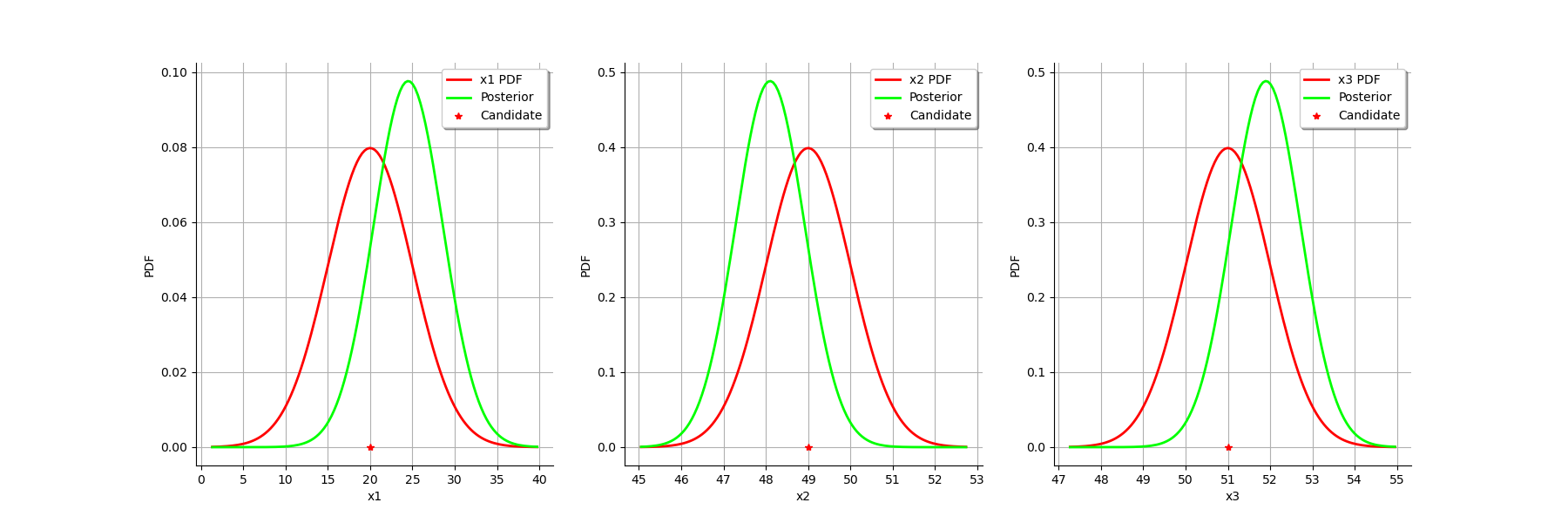
The two distributions are different, which shows that the calibration is sensible to the observations (if the observations were not sensible, the two distributions were superimposed). Moreover, the two distributions are quite close, which implies that the prior distribution has played a roled in the calibration (otherwise the two distributions would be completely different, indicating that only the observations were taken into account).
Gaussian nonlinear calibration¶
The GaussianNonLinearCalibration class performs Gaussian nonlinear calibration.
algo = ot.GaussianNonLinearCalibration(
mycf, Qobs, Hobs, thetaPrior, sigma, errorCovariance
)
The run method computes the solution of the problem.
algo.run()
calibrationResult = algo.getResult()
Analysis of the results¶
The getParameterMAP method returns the maximum of the posterior distribution of .
thetaStar = calibrationResult.getParameterMAP()
print(thetaStar)
[30.5205,47.6341,52.3659]
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsInputs()
graph.setLegendPosition("topleft")
view = viewer.View(graph)
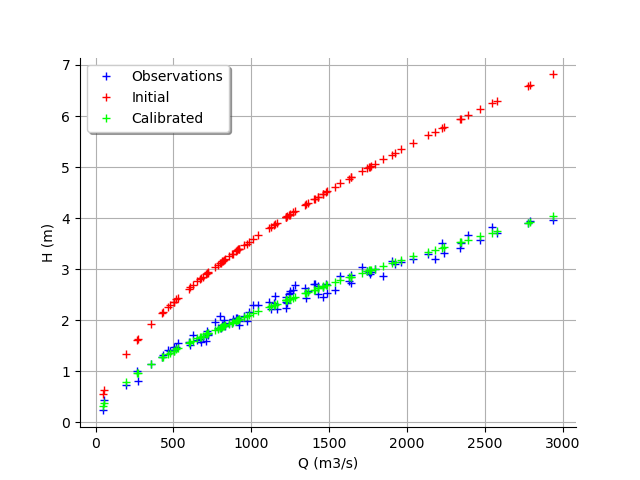
We see that the output of the model after calibration is in the middle of the observations: the calibration seems correct.
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsPredictions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
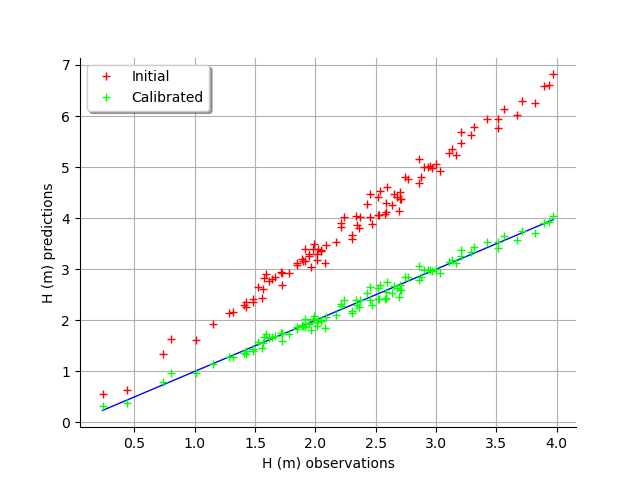
The fit is excellent after calibration. Indeed, the cloud of points after calibration is on the diagonal.
graph = calibrationResult.drawResiduals()
view = viewer.View(graph)
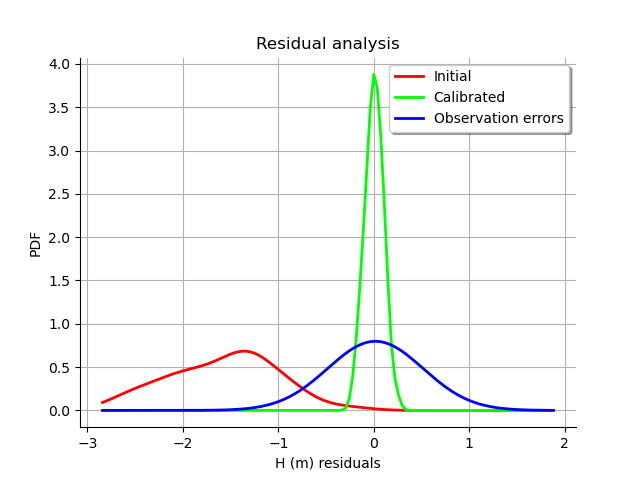
We see that the histogram of the residual is centered on zero. This is a proof that the calibration did perform correctly.
The getParameterPosterior method returns the posterior normal distribution of .
distributionPosterior = calibrationResult.getParameterPosterior()
We can compute a 95% confidence interval of the parameter .
print(
distributionPosterior.computeBilateralConfidenceIntervalWithMarginalProbability(
0.95
)[0]
)
[30.483, 31.0367]
[47.5681, 47.6389]
[52.3611, 52.4319]
We see that there is a small uncertainty on the value of all parameters.
We can compare the prior and posterior distributions of the marginals of .
graph = calibrationResult.drawParameterDistributions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
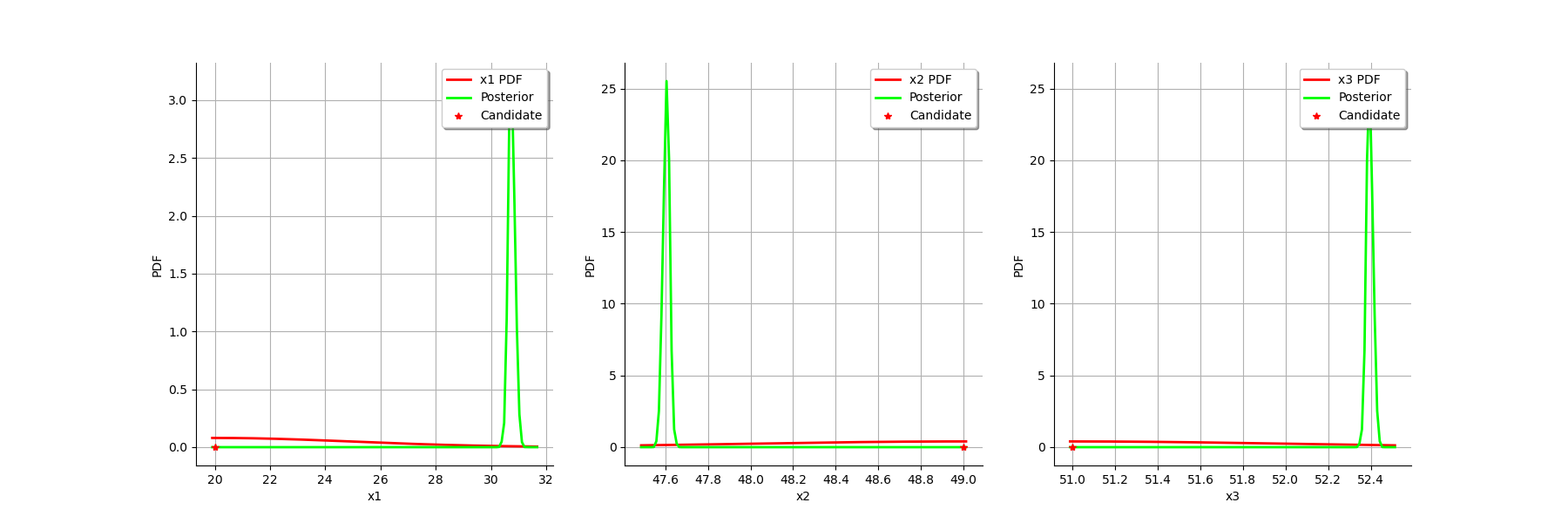
The two distributions are very different, with a spiky posterior distribution. This shows that the calibration is very sensible to the observations.
Tuning the posterior distribution estimation¶
The “GaussianNonLinearCalibration-BootstrapSize” key controls the posterior distribution estimation.
If “GaussianNonLinearCalibration-BootstrapSize” > 0 (by default it is equal to 100), then a bootstrap resample algorithm is used to see the dispersion of the MAP estimator. This allows one to see the variability of the estimator with respect to the finite observation sample.
If “GaussianNonLinearCalibration-BootstrapSize” is zero, then the Gaussian linear calibration estimator is used (i.e. the GaussianLinearCalibration class) at the optimum. This is called the Laplace approximation.
We must configure the key before creating the object (otherwise changing the parameter does not change the result).
ot.ResourceMap.SetAsUnsignedInteger("GaussianNonLinearCalibration-BootstrapSize", 0)
algo = ot.GaussianNonLinearCalibration(
mycf, Qobs, Hobs, thetaPrior, sigma, errorCovariance
)
algo.run()
calibrationResult = algo.getResult()
graph = calibrationResult.drawParameterDistributions()
viewer = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
As we can see, this does not change much the posterior distribution, which remains spiky.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 5.112 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS