Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Logistic growth model¶
In this example, we use the logistic growth model in order to show how to define a function which has a vector input and a field output. We use the OpenTURNSPythonPointToFieldFunction class to define the derived class and its methods.
Define the model¶
from openturns.usecases import logistic_model
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
We load the logistic model from the usecases module :
lm = logistic_model.LogisticModel()
We get the data from the LogisticModel data class (22 dates with population) :
ustime = lm.data.getMarginal(0)
uspop = lm.data.getMarginal(1)
We get the input parameters distribution distX :
distX = lm.distX
We define the model :
class Popu(ot.OpenTURNSPythonPointToFieldFunction):
def __init__(self, t0=1790.0, tfinal=2000.0, nt=1000):
grid = ot.RegularGrid(t0, (tfinal - t0) / (nt - 1), nt)
super(Popu, self).__init__(3, grid, 1)
self.setInputDescription(["y0", "a", "b"])
self.setOutputDescription(["N"])
self.ticks_ = [t[0] for t in grid.getVertices()]
self.phi_ = ot.SymbolicFunction(["t", "y", "a", "b"], ["a*y - b*y^2"])
def _exec(self, X):
y0 = X[0]
a = X[1]
b = X[2]
phi_ab = ot.ParametricFunction(self.phi_, [2, 3], [a, b])
phi_t = ot.ParametricFunction(phi_ab, [0], [0.0])
solver = ot.RungeKutta(phi_t)
initialState = [y0]
values = solver.solve(initialState, self.ticks_)
return values * [1.0e-6]
F = Popu(1790.0, 2000.0, 1000)
popu = ot.PointToFieldFunction(F)
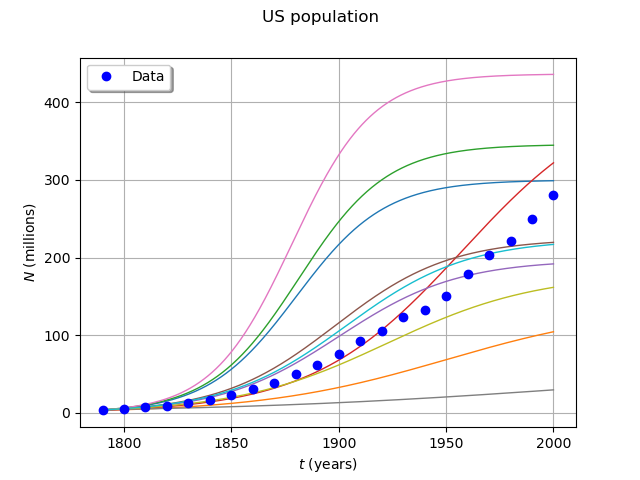
Generate a sample from the model¶
Sample from the model
size = 10
inputSample = distX.getSample(size)
outputSample = popu(inputSample)
ot.ResourceMap.SetAsUnsignedInteger("Drawable-DefaultPalettePhase", size)
Draw some curves
graph = outputSample.drawMarginal(0)
graph.setTitle("US population")
graph.setXTitle(r"$t$ (years)")
graph.setYTitle(r"$N$ (millions)")
cloud = ot.Cloud(ustime, uspop)
cloud.setPointStyle("circle")
cloud.setLegend("Data")
graph.add(cloud)
graph.setLegendPosition("topleft")
view = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.243 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS