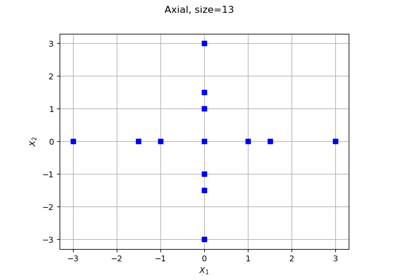
StratifiedExperiment¶
- class StratifiedExperiment(*args)¶
Base class for stratified experiments.
- Available constructor:
StratifiedExperiment(center, levels)
- Parameters:
- center, levelstwo sequences of float
Sequences which have different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
Notes
A StratifiedExperiment object can be used only through its derived classes:
Methods
generate()Generate points according to the type of the experiment.
Get the center of the stratified experiment.
Accessor to the object's name.
getId()Accessor to the object's id.
Get the levels of the stratified experiment.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
Accessor to the object's visibility state.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
setCenter(center)Set the center of the stratified experiment.
setLevels(levels)Set the levels of the stratified experiment.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setShadowedId(id)Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
setVisibility(visible)Accessor to the object's visibility state.
- __init__(*args)¶
- generate()¶
Generate points according to the type of the experiment.
- Returns:
- sample
Sample The points which constitute the design of experiments. The sampling method is defined by the nature of the experiment.
- sample
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0) >>> myExperiment = ot.Experiment(ot.MonteCarloExperiment(ot.Normal(2),5)) >>> print(myExperiment.generate()) [ X0 X1 ] 0 : [ 0.608202 -1.26617 ] 1 : [ -0.438266 1.20548 ] 2 : [ -2.18139 0.350042 ] 3 : [ -0.355007 1.43725 ] 4 : [ 0.810668 0.793156 ]
- getCenter()¶
Get the center of the stratified experiment.
- Returns:
- center
Point Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- center
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getId()¶
Accessor to the object’s id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getLevels()¶
Get the levels of the stratified experiment.
- Returns:
- levels
Point Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- levels
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getShadowedId()¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getVisibility()¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Returns:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- hasVisibleName()¶
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
- Returns:
- hasVisibleNamebool
True if the name is not empty and not the default one.
- setCenter(center)¶
Set the center of the stratified experiment.
- Parameters:
- centersequence of float
Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- setLevels(levels)¶
Set the levels of the stratified experiment.
- Parameters:
- levelssequence of float
Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setShadowedId(id)¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Parameters:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- setVisibility(visible)¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Parameters:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
Examples using the class¶
Use the FORM algorithm in case of several design points
An illustrated example of a FORM probability estimate
Example of sensitivity analyses on the wing weight model
Create mixed deterministic and probabilistic designs of experiments
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS