Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Multi-objective optimization using Pagmo¶
In this example we are going to explore optimization using the Pagmo solver.
import openturns as ot
from openturns.viewer import View
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0)
List available algorithms
for algo in ot.Pagmo.GetAlgorithmNames():
print(algo)
gaco
de
sade
de1220
gwo
ihs
pso
pso_gen
sea
sga
simulated_annealing
bee_colony
cmaes
xnes
nsga2
moead
moead_gen
mhaco
nspso
Create the problem, from ZDT test suite
f = ot.SymbolicFunction(
["x1", "x2"], ["x1", "var g := 1.0 + 9.0 * (x1 + x2); g * (1.0 - sqrt(x1 / g))"]
)
zdt1 = ot.OptimizationProblem(f)
zdt1.setBounds(ot.Interval([0.0] * 2, [1.0] * 2))
We create the first generation of points by sampling into the bounding box
pop0 = ot.ComposedDistribution([ot.Uniform(0.0, 1.0)] * 2).getSample(100)
We create the algorithm that should evolve over 10 generations
algo = ot.Pagmo(zdt1, "nsga2", pop0)
algo.setGenerationNumber(10)
Benefit from parallel evaluations if the function allows it
algo.setBlockSize(8)
We run the algo
algo.run()
pop1 = algo.getResult().getFinalPoints()
We list the available Pareto fronts
fronts = algo.getResult().getParetoFrontsIndices()
len(fronts)
9
We show the Pareto front
graph = ot.Graph("Pareto front", "y1", "y2", True, "topright")
front = algo.getResult().getFinalValues().select(fronts[0]).sortAccordingToAComponent(0)
data = ot.Sample(2 * front.getSize() - 1, 2)
for i in range(front.getSize()):
data[2 * i] = front[i]
if i != front.getSize() - 1:
data[2 * i + 1, 0] = front[i + 1, 0]
data[2 * i + 1, 1] = front[i, 1]
curve = ot.Curve(data)
curve.setColor("blue")
curve.setLegend(f"front {0}")
graph.add(curve)
graph.setGrid(True)
_ = View(graph)
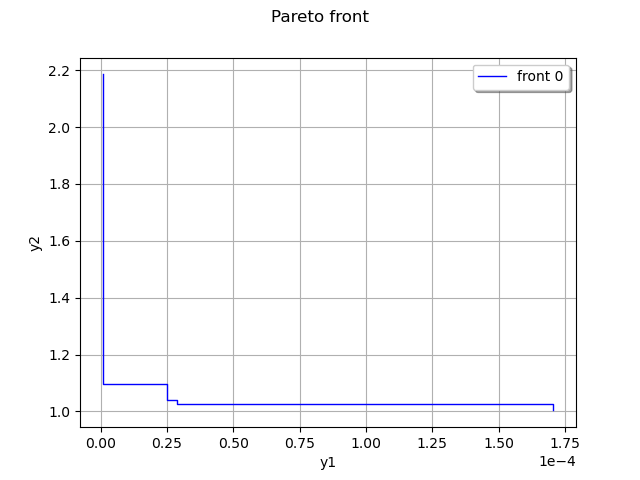
We show the Pareto front from successive generations
fronts = []
for gen in range(5):
algo = ot.Pagmo(zdt1, "nsga2", pop0)
algo.setGenerationNumber(gen)
algo.run()
front0 = algo.getResult().getParetoFrontsIndices()[0]
fronts.append(algo.getResult().getFinalValues().select(front0))
graph = ot.Graph("Successive fronts", "y1", "y2", True, "topright")
palette = ot.Drawable.BuildDefaultPalette(len(fronts))
for k in range(len(fronts)):
front = fronts[k].sortAccordingToAComponent(0)
print(front)
data = ot.Sample(2 * front.getSize() - 1, 2)
for i in range(front.getSize()):
data[2 * i] = front[i]
if i != front.getSize() - 1:
data[2 * i + 1, 0] = front[i + 1, 0]
data[2 * i + 1, 1] = front[i, 1]
curve = ot.Curve(data)
curve.setColor(palette[k])
curve.setLegend(f"generation {k}")
graph.add(curve)
graph.setGrid(True)
_ = View(graph)
View.ShowAll()
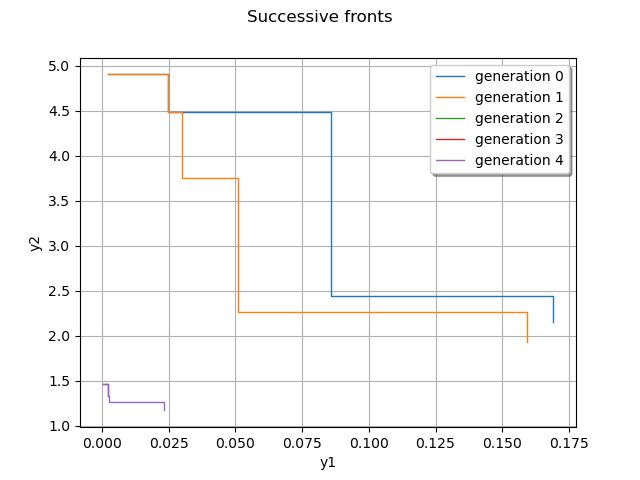
[ v0 v1 ]
0 : [ 0.00210762 4.90217 ]
1 : [ 0.0245595 4.48078 ]
2 : [ 0.085785 2.443 ]
3 : [ 0.169217 2.15559 ]
[ v0 v1 ]
0 : [ 0.00210762 4.90217 ]
1 : [ 0.0245595 4.48078 ]
2 : [ 0.0245595 4.48078 ]
3 : [ 0.0301332 3.74995 ]
4 : [ 0.0509366 2.2659 ]
5 : [ 0.159386 1.93377 ]
[ v0 v1 ]
0 : [ 0.00210762 1.44946 ]
[ v0 v1 ]
0 : [ 0.000163801 1.46979 ]
1 : [ 0.00210762 1.33046 ]
[ v0 v1 ]
0 : [ 0.000163801 1.46979 ]
1 : [ 0.000163801 1.46979 ]
2 : [ 0.00210762 1.33046 ]
3 : [ 0.00260066 1.26379 ]
4 : [ 0.0233772 1.17114 ]
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS