Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Create a general linear model metamodel¶
In this example we are going to create a global approximation of a model response using a general linear model. We show how to use the GeneralLinearModelAlgorithm class, which estimates the parameters of the model.
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
We create a model and a sample from this model.
ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0)
dimension = 2
input_names = ["x1", "x2"]
formulas = ["cos(x1 + x2)"]
model = ot.SymbolicFunction(input_names, formulas)
distribution = ot.Normal(dimension)
x = distribution.getSample(100)
y = model(x)
We create a GeneralLinearModelAlgorithm based on a linear basis. The run method estimats the coefficients of the trend and the hyperparameters of the covariance model.
basis = ot.LinearBasisFactory(dimension).build()
covarianceModel = ot.SquaredExponential([1] * dimension, [1.0])
algo = ot.GeneralLinearModelAlgorithm(x, y, covarianceModel, basis)
algo.run()
result = algo.getResult()
We see that the trend coefficients have been estimated.
result.getTrendCoefficients()
The parameters of the covariance models also have been estimated.
result.getCovarianceModel()
The getMetaModel method returns the metamodel where the parameters have been estimated.
responseSurface = result.getMetaModel()
Plot the output of our model depending on x2 with x1=0.5.
xmin = -5.0
xmax = 5.0
x1value = 0.5
parametricModelGraph = ot.ParametricFunction(model, [0], [x1value]).draw(xmin, xmax)
parametricModelGraph.setColors(["red"])
graphMetamodel = ot.ParametricFunction(responseSurface, [0], [x1value]).draw(xmin, xmax)
graphMetamodel.setColors(["blue"])
parametricModelGraph.add(graphMetamodel)
parametricModelGraph.setLegends(["Model", "Meta-Model"])
parametricModelGraph.setLegendPosition("upper right")
view = viewer.View(parametricModelGraph)
plt.show()
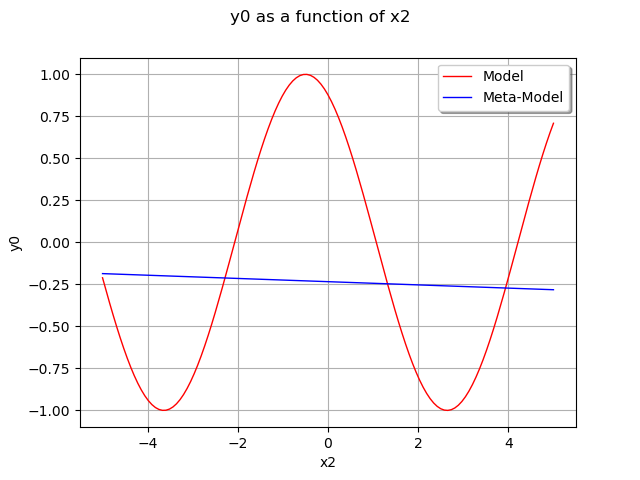
We see that the metamodel is equal to the trend because it takes into account the fact that the mean of the gaussian process is zero.
This GeneralLinearModelAlgorithm class is the main building block of the KrigingAlgorithm. This is why most basic use cases are based on the KrigingAlgorithm instead of the GeneralLinearModelAlgorithm, because this allows one to condition the gaussian process.
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS