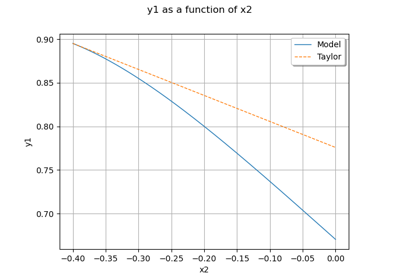
LinearTaylor¶
- class LinearTaylor(*args)¶
First order polynomial response surface by Taylor expansion.
- Available constructors:
LinearTaylor(center, function)
- Parameters:
- centersequence of float
Point
.
- function
Function Function
to be approximated at the point
.
Notes
The response surface is the first-order Taylor expansion of the function
at the point
. Refer to Taylor Expansion for details.
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> formulas = ['x1 * sin(x2)', 'cos(x1 + x2)', '(x2 + 1) * exp(x1 - 2 * x2)'] >>> myFunc = ot.SymbolicFunction(['x1', 'x2'], formulas) >>> myTaylor = ot.LinearTaylor([1, 2], myFunc) >>> myTaylor.run() >>> responseSurface = myTaylor.getMetaModel() >>> print(responseSurface([1.2,1.9])) [1.13277,-1.0041,0.204127]
Methods
Get the center.
Accessor to the object's name.
Get the constant vector of the approximation.
getId()Accessor to the object's id.
Get the function.
Get the gradient of the function at
.
Get the polynomial approximation of the function.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
Accessor to the object's visibility state.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
run()Perform the first-order Taylor expansion around
.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setShadowedId(id)Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
setVisibility(visible)Accessor to the object's visibility state.
- __init__(*args)¶
- getCenter()¶
Get the center.
- Returns:
- center
Point Point
where the Taylor expansion of the function is performed.
- center
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getId()¶
Accessor to the object’s id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getMetaModel()¶
Get the polynomial approximation of the function.
- Returns:
- approximation
Function The first-order Taylor expansiosn of
at
.
- approximation
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getShadowedId()¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getVisibility()¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Returns:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- hasVisibleName()¶
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
- Returns:
- hasVisibleNamebool
True if the name is not empty and not the default one.
- run()¶
Perform the first-order Taylor expansion around
.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setShadowedId(id)¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Parameters:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- setVisibility(visible)¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Parameters:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
Examples using the class¶
Using the FORM - SORM algorithms on a nonlinear function
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS