Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Define a connection function with a field output¶
In this example, we define a function which has a vector input and a field output.
The goal of this example is to show how to use PointToFieldConnection class to combine two functions.
A detailed explanation of the model is presented here.
Define the model¶
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as otv
from openturns.usecases import viscous_free_fall
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
Load the viscous free fall example.
vff = viscous_free_fall.ViscousFreeFall()
distribution = vff.distribution
model = vff.model
Restrict the number of inputs¶
We define a function which has input only z0 as input to freeze the 3 other inputs of the original model:
fz0 = ot.SymbolicFunction(["z0"], ["z0", "55", "80", "15"])
Then we use the PointToFieldConnection to compose it with the original model.
model_z0 = ot.PointToFieldConnection(model, fz0)
Sample trajectories¶
In order to sample trajectories, we use the getSample method of the distribution of z0 and apply the field function.
size = 10
inputSample = vff.distZ0.getSample(size)
outputSample = model_z0(inputSample)
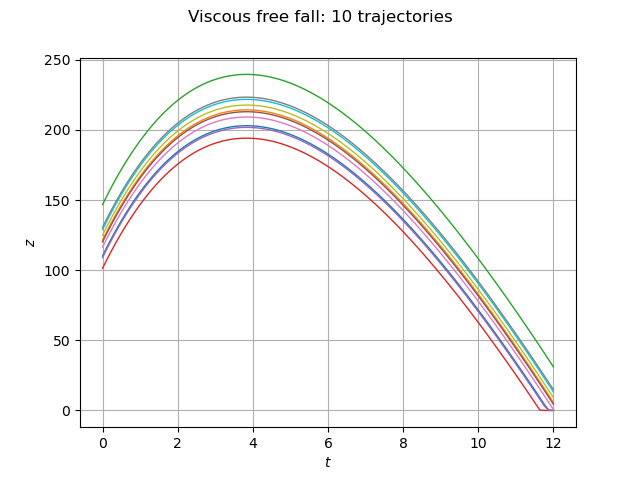
Draw viscous free fall trajectories.
graph = outputSample.drawMarginal(0)
graph.setTitle("Viscous free fall: %d trajectories" % (size))
graph.setXTitle(r"$t$")
graph.setYTitle(r"$z$")
view = otv.View(graph)
otv.View.ShowAll()
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS