PostAnalyticalImportanceSampling¶
- class PostAnalyticalImportanceSampling(*args)¶
Post analytical importance sampling.
Simulation method where the original distribution is replaced by the distribution in the standard space centered around the provided design point.
This method, based on importance sampling, uses a normal instrumental distribution in the standard space (see [lemaire2009] page 255, [melchers1990]).
- Parameters:
- analyticalResult
AnalyticalResult Result which contains the whole information on the analytical study performed before the simulation study: in particular, the standard distribution of the standard space and the standard space design point.
- analyticalResult
See also
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> f = ot.SymbolicFunction(['E', 'F', 'L', 'I'], ['-F*L^3/(3*E*I)']) >>> distribution = ot.Normal([50.0, 1.0, 10.0, 5.0], [1.0]*4, ot.IdentityMatrix(4)) >>> X = ot.RandomVector(distribution) >>> Y = ot.CompositeRandomVector(f, X) >>> event = ot.ThresholdEvent(Y, ot.Less(), -3.0) >>> solver = ot.AbdoRackwitz() >>> analytical = ot.FORM(solver, event, [50.0, 1.0, 10.0, 5.0]) >>> analytical.run() >>> analyticalResult = analytical.getResult() >>> algo = ot.PostAnalyticalImportanceSampling(analyticalResult) >>> algo.run() >>> result = algo.getResult() >>> pf = result.getProbabilityEstimate()
Methods
drawProbabilityConvergence(*args)Draw the probability convergence at a given level.
Accessor to the analytical result.
Accessor to the block size.
Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the control probability.
Accessor to the convergence strategy.
getEvent()Accessor to the event.
Accessor to the maximum coefficient of variation.
Accessor to the maximum sample size.
Accessor to the maximum standard deviation.
Accessor to the maximum duration.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the results.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
run()Launch simulation.
setBlockSize(blockSize)Accessor to the block size.
setConvergenceStrategy(convergenceStrategy)Accessor to the convergence strategy.
Accessor to the maximum coefficient of variation.
setMaximumOuterSampling(maximumOuterSampling)Accessor to the maximum sample size.
Accessor to the maximum standard deviation.
setMaximumTimeDuration(maximumTimeDuration)Accessor to the maximum duration.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setProgressCallback(*args)Set up a progress callback.
setStopCallback(*args)Set up a stop callback.
- __init__(*args)¶
- drawProbabilityConvergence(*args)¶
Draw the probability convergence at a given level.
- Parameters:
- levelfloat, optional
The probability convergence is drawn at this given confidence length level. By default level is 0.95.
- Returns:
- grapha
Graph probability convergence graph
- grapha
- getAnalyticalResult()¶
Accessor to the analytical result.
- Returns:
- result
AnalyticalResult Result of the analytical study which has been performed just before the simulation study centered around the importance factor.
- result
- getBlockSize()¶
Accessor to the block size.
- Returns:
- blockSizeint
Number of terms in the probability simulation estimator grouped together. It is set by default to 1.
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getControlProbability()¶
Accessor to the control probability.
- Returns:
- pfloat,
The probability of the analytical result.
Notes
The control probability
is deduced from the corresponding analytical result:
where
denotes the Hasofer reliability index and
the univariate standard CDF of the elliptical distribution in the standard space.
- getConvergenceStrategy()¶
Accessor to the convergence strategy.
- Returns:
- storage_strategy
HistoryStrategy Storage strategy used to store the values of the probability estimator and its variance during the simulation algorithm.
- storage_strategy
- getEvent()¶
Accessor to the event.
- Returns:
- event
RandomVector Event we want to evaluate the probability.
- event
- getMaximumCoefficientOfVariation()¶
Accessor to the maximum coefficient of variation.
- Returns:
- coefficientfloat
Maximum coefficient of variation of the simulated sample.
- getMaximumOuterSampling()¶
Accessor to the maximum sample size.
- Returns:
- outerSamplingint
Maximum number of groups of terms in the probability simulation estimator.
- getMaximumStandardDeviation()¶
Accessor to the maximum standard deviation.
- Returns:
- sigmafloat,
Maximum standard deviation of the estimator.
- sigmafloat,
- getMaximumTimeDuration()¶
Accessor to the maximum duration.
- Returns:
- maximumTimeDurationfloat
Maximum optimization duration in seconds.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getResult()¶
Accessor to the results.
- Returns:
- results
SimulationResult Structure containing all the results obtained after simulation and created by the method
run().
- results
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- run()¶
Launch simulation.
See also
Notes
It launches the simulation and creates a
SimulationResult, structure containing all the results obtained after simulation. It computes the probability of occurrence of the given event by computing the empirical mean of a sample of size at most outerSampling * blockSize, this sample being built by blocks of size blockSize. It allows one to use efficiently the distribution of the computation as well as it allows one to deal with a sample sizeby a combination of blockSize and outerSampling.
- setBlockSize(blockSize)¶
Accessor to the block size.
- Parameters:
- blockSizeint,
Number of terms in the probability simulation estimator grouped together. It is set by default to 1.
- blockSizeint,
Notes
For Monte Carlo, LHS and Importance Sampling methods, this allows one to save space while allowing multithreading, when available we recommend to use the number of available CPUs; for the Directional Sampling, we recommend to set it to 1.
- setConvergenceStrategy(convergenceStrategy)¶
Accessor to the convergence strategy.
- Parameters:
- storage_strategy
HistoryStrategy Storage strategy used to store the values of the probability estimator and its variance during the simulation algorithm.
- storage_strategy
- setMaximumCoefficientOfVariation(maximumCoefficientOfVariation)¶
Accessor to the maximum coefficient of variation.
- Parameters:
- coefficientfloat
Maximum coefficient of variation of the simulated sample.
- setMaximumOuterSampling(maximumOuterSampling)¶
Accessor to the maximum sample size.
- Parameters:
- outerSamplingint
Maximum number of groups of terms in the probability simulation estimator.
- setMaximumStandardDeviation(maximumStandardDeviation)¶
Accessor to the maximum standard deviation.
- Parameters:
- sigmafloat,
Maximum standard deviation of the estimator.
- sigmafloat,
- setMaximumTimeDuration(maximumTimeDuration)¶
Accessor to the maximum duration.
- Parameters:
- maximumTimeDurationfloat
Maximum optimization duration in seconds.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setProgressCallback(*args)¶
Set up a progress callback.
Can be used to programmatically report the progress of a simulation.
- Parameters:
- callbackcallable
Takes a float as argument as percentage of progress.
Examples
>>> import sys >>> import openturns as ot >>> experiment = ot.MonteCarloExperiment() >>> X = ot.RandomVector(ot.Normal()) >>> Y = ot.CompositeRandomVector(ot.SymbolicFunction(['X'], ['1.1*X']), X) >>> event = ot.ThresholdEvent(Y, ot.Less(), -2.0) >>> algo = ot.ProbabilitySimulationAlgorithm(event, experiment) >>> algo.setMaximumOuterSampling(100) >>> algo.setMaximumCoefficientOfVariation(-1.0) >>> def report_progress(progress): ... sys.stderr.write('-- progress=' + str(progress) + '%\n') >>> algo.setProgressCallback(report_progress) >>> algo.run()
- setStopCallback(*args)¶
Set up a stop callback.
Can be used to programmatically stop a simulation.
- Parameters:
- callbackcallable
Returns an int deciding whether to stop or continue.
Examples
Stop a Monte Carlo simulation algorithm using a time limit
>>> import openturns as ot >>> experiment = ot.MonteCarloExperiment() >>> X = ot.RandomVector(ot.Normal()) >>> Y = ot.CompositeRandomVector(ot.SymbolicFunction(['X'], ['1.1*X']), X) >>> event = ot.ThresholdEvent(Y, ot.Less(), -2.0) >>> algo = ot.ProbabilitySimulationAlgorithm(event, experiment) >>> algo.setMaximumOuterSampling(10000000) >>> algo.setMaximumCoefficientOfVariation(-1.0) >>> algo.setMaximumTimeDuration(0.1) >>> algo.run()
Examples using the class¶
Use the post-analytical importance sampling algorithm
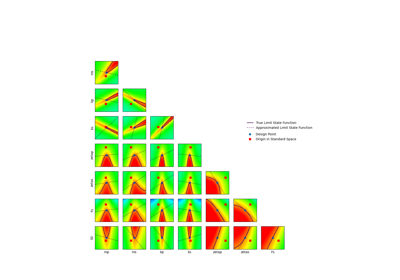
Using the FORM - SORM algorithms on a nonlinear function
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS