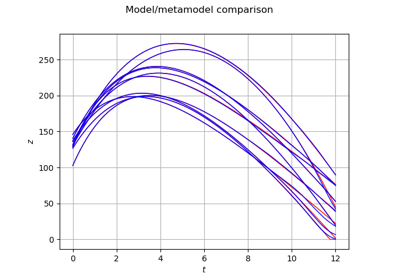
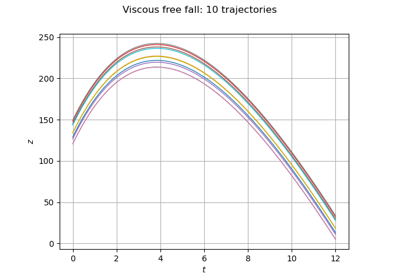
A viscous free fall example¶
Introduction¶
We consider an object inside a vertical cylinder which contains a viscous fluid. The fluid generates a drag force which limits the speed of the solid and we assume that the force depends linearily on the object speed:
for any where:
is the speed
,
is the time
,
is the maximum time
,
is the gravitational acceleration
,
is the mass
,
is the linear drag coefficient
.
The exact solution of the previous differential equation is:
for any
where:
is the altitude above the surface
,
is the initial altitude
,
is the initial speed (upward)
,
is the limit speed
:
is time caracteristic
:
The stationnary speed limit at infinite time is equal to :
When there is no drag, i.e. when , the trajectory depends quadratically on
:
for any .
Furthermore when the solid touches the ground, we ensure that the altitude remains nonnegative i.e. the final altitude is:
for any .
Probabilistic model¶
The parameters ,
,
and
are probabilistic:
,
,
,
.
References¶
Steven C. Chapra. Applied numerical methods with Matlab for engineers and scientists, Third edition. 2012. Chapter 7, “Optimization”, p.182.
API documentation¶
- class ViscousFreeFall
Data class for the viscous free fall.
- Attributes:
- dimint
The dimension of the problem, dim=4.
- outputDimensionint
The output dimension of the problem, outputDimension=1.
- tminfloat
Minimum time, tmin = 0.0
- tmaxfloat
Maximum time, tmax = 12.0
- gridsizeint
Number of time steps, gridsize = 100.
- mesh
Mesh Time grid
- vertices
Sample Vertices of the mesh
- distZ0
Uniform Distribution of the initial altitude: Uniform(100.0, 150.0)
- distV0
Normal Distribution of the initial speed: Normal(55.0, 10.0)
- distM
Normal Distribution of the mass: Normal(80.0, 8.0)
- distC
Uniform Distribution of the drag: Uniform(0.0, 30.0)
- distribution
JointDistribution The joint distribution of the input parameters.
- model
PythonPointToFieldFunction The exact solution of the fall
Examples
>>> from openturns.usecases import viscous_free_fall >>> # Load the viscous free fall example >>> vff = viscous_free_fall.ViscousFreeFall()
Examples based on this use case¶
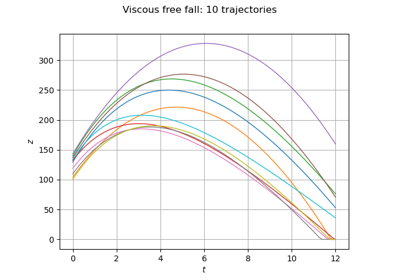
Define a function with a field output: the viscous free fall example
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS