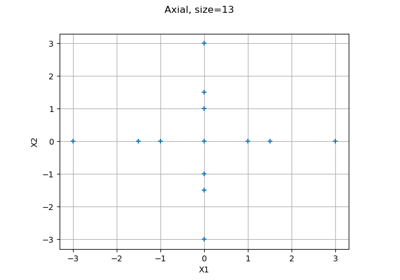
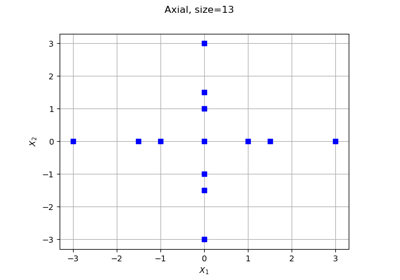
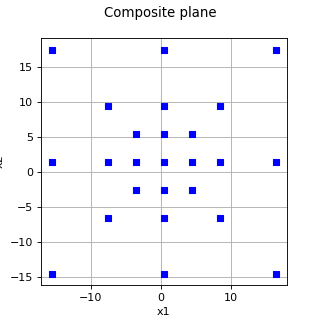
Composite¶
(Source code, png)
- class Composite(*args)¶
Composite design of experiments.
- Available constructor:
Composite(center, levels)
Composite(dimension, levels)
- Parameters:
- centersequence of float
Center of the design of experiments. If not specified, the design of experiments is centered on
.
- levelssequence of float of dimension
The discretization of directions (the same for each one), without any consideration of unit.
- dimensionpositive int
Dimension
of the space where the design of experiments is created.
Methods
generate()Generate points according to the type of the experiment.
Get the center of the stratified experiment.
Accessor to the object's name.
Get the levels of the stratified experiment.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
setCenter(center)Set the center of the stratified experiment.
setLevels(levels)Set the levels of the stratified experiment.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
See also
Notes
Composite is a stratified design of experiments enabling to create a pattern as the union of an
Axialpattern and aFactorialone. The number of points generated is.
In order to scale each direction and translate the grid structure onto the proper center, use the operator
and
of
Sample.Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> levels = [4.0, 2.0, 7.0] >>> myCenteredReductedGrid = ot.Composite(2, levels) >>> mySample = myCenteredReductedGrid.generate() >>> # Translate the grid >>> mySample+=4 >>> # Scale each direction >>> mySample*=2
- __init__(*args)¶
- generate()¶
Generate points according to the type of the experiment.
- Returns:
- sample
Sample The points which constitute the design of experiments. The sampling method is defined by the nature of the experiment.
- sample
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0) >>> myExperiment = ot.Experiment(ot.MonteCarloExperiment(ot.Normal(2),5)) >>> print(myExperiment.generate()) [ X0 X1 ] 0 : [ 0.608202 -1.26617 ] 1 : [ -0.438266 1.20548 ] 2 : [ -2.18139 0.350042 ] 3 : [ -0.355007 1.43725 ] 4 : [ 0.810668 0.793156 ]
- getCenter()¶
Get the center of the stratified experiment.
- Returns:
- center
Point Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- center
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getLevels()¶
Get the levels of the stratified experiment.
- Returns:
- levels
Point Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- levels
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- setCenter(center)¶
Set the center of the stratified experiment.
- Parameters:
- centersequence of float
Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- setLevels(levels)¶
Set the levels of the stratified experiment.
- Parameters:
- levelssequence of float
Sequence which has different meanings according to the nature of the stratified experiment: Axial, Composite, Factorial or Box (see corresponding documentation).
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS