LatentVariableModel¶
- class LatentVariableModel(*args)¶
Latent variable covariance function.
Warning
This class is experimental and likely to be modified in future releases. To use it, import the
openturns.experimentalsubmodule.- Parameters:
- nLevelsint
Number of levels
characterizing the categorical variable.
- latentDimint
The dimension
of the latent space onto which the categorical variable levels are projected.
Methods
activateAmplitude(isAmplitudeActive)Activate/deactivate the amplitude parameter(s).
activateNuggetFactor(isNuggetFactorActive)Activate/deactivate the nugget factor.
activateScale(isScaleActive)Activate/deactivate the scale parameter(s).
computeAsScalar(*args)Compute the covariance function for scalar model.
computeCrossCovariance(*args)Compute the covariance function on a given mesh.
discretize(*args)Discretize the covariance function on a given mesh.
discretizeAndFactorize(*args)Discretize and factorize the covariance function on a given mesh.
Discretize and factorize the covariance function on a given mesh.
discretizeHMatrix(*args)Discretize the covariance function on a given mesh using HMatrix result.
discretizeRow(vertices, p)(TODO)
draw(*args)Not yet implemented
Active latent variables accessor.
Accessor to the active parameter set.
Get the amplitude parameter
of the covariance function.
Accessor to the object's name.
Latent variables accessor.
Get the full parameters of the covariance function.
Get the description full parameters of the covariance function.
Get the input dimension
of the covariance function.
Latent dimension accessor.
Level number accessor.
getMarginal(*args)Get the ith marginal of the model.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the nugget factor.
Get the spatial correlation matrix
of the covariance function.
Get the dimension
of the covariance function.
Get the parameters of the covariance function.
Get the description of the covariance function parameters.
getScale()Get the scale parameter
of the covariance function.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
Test whether the model is diagonal or not.
Test whether the model is stationary or not.
parameterGradient(s, t)Compute the gradient according to the parameters.
partialGradient(s, t)Compute the gradient of the covariance function.
setActiveParameter(active)Accessor to the active parameter set.
setAmplitude(amplitude)Set the amplitude parameter
of the covariance function.
setFullParameter(parameter)Set the full parameters of the covariance function.
setLatentVariables(latentVariablesCoordinates)Number of levels accessor.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setNuggetFactor(nuggetFactor)Set the nugget factor for the variance of the observation error.
setOutputCorrelation(correlation)Set the spatial correlation matrix
of the covariance function.
setParameter(parameter)Set the parameters of the covariance function.
setScale(scale)Set the scale parameter
of the covariance function.
See also
Notes
The Latent variable covariance function is a covariance model allowing to compute the covariance between different unordered values (or levels) of a categorical variable
.
The underlying idea is that each categorical level is mapped onto a distinct point in a
-dimensional latent space. The covariance between the various levels is then computed as the
SquaredExponentialcovariance between the mappings in the latent space. Letbe the mapping function, the covariance function between two discrete values
and
is computed as:
The coordinates of the mapping points are part of the covariance model parameters, together with the latent squared exponential model scale and amplitude. It is important to note that in order to compensate for possible rotations and translations of the mapping points, the coordinates of the first level mapping are fixed to the latent space origin, whereas all of the coordinates of the second level mapping are fixed to
, except for the first one. As a result, the number of active latent variable coordinates is equal to:
In practice, the class distinguishes between the fullLatentVariables attribute, which contains the actual latent variables coordinates, and the activeLatentVariables attribute, which contains only the coordinates that can be modified. Additional information can be found in [zhang2020].
Is is important to note that for the sake of simplicity, the categorical variable levels must be represented as integers, ranging from
to
. However, this representation is purely practical, and the actual values assigned to each level have no practical meaning or effect: only the latent variables coordinates have an effect on the covariance value. Moreover, these categorical variables, which are encoded using numerical values, can be of a non-numerical nature (e.g., types of material, architectural choices, colors, etc.).
Finally, for a similar reason, when using this type of kernel when defining a Gaussian process, it is suggested to rely on a constant functional basis: please use the
ConstantBasisFactoryclass.Examples
Create a latent model covariance function with a latent space of dimension 2, for a categorical variable characterized by 3 levels:
>>> import openturns.experimental as otexp >>> covModel = otexp.LatentVariableModel(3, 2) >>> activeCoordinates = [0.1, 0.3, -0.4] >>> covModel.setLatentVariables(activeCoordinates) >>> print(covModel(1, 2)) [[ 0.904837 ]] >>> print(covModel(0, 2)) [[ 0.882497 ]] >>> print(covModel(1, 1)) [[ 1 ]]
- __init__(*args)¶
- activateAmplitude(isAmplitudeActive)¶
Activate/deactivate the amplitude parameter(s).
In the context of Kriging, defines whether amplitude parameters should be tuned.
- Parameters:
- isAmplitudeActivebool
If True, the amplitude parameters are all tuned. If False, none of them is tuned.
- activateNuggetFactor(isNuggetFactorActive)¶
Activate/deactivate the nugget factor.
In the context of Kriging, defines whether the nugget factor should be tuned.
- Parameters:
- isNuggetFactorActivebool
If True (resp. False), the nugget factor is (resp. is not) tuned.
- activateScale(isScaleActive)¶
Activate/deactivate the scale parameter(s).
In the context of Kriging, defines whether scale parameters should be tuned.
- Parameters:
- isScaleActivebool
If True, the scale parameters are all tuned. If False, none of them is tuned.
- computeAsScalar(*args)¶
Compute the covariance function for scalar model.
- Parameters:
- s, tfloats
Must have integer values between
and
- Returns:
- covariancefloat
Covariance.
Notes
The method makes sense only if the dimension of the process is
. It evaluates
.
- computeCrossCovariance(*args)¶
Compute the covariance function on a given mesh.
- Parameters:
- Returns:
- Matrix
Matrix Cross covariance matrix
- Matrix
Notes
This method computes a cross-covariance matrix. The cross-covariance is the evaluation of the covariance model on both firstVertices and secondVertices.
If firstVertices contains
points and secondVertices contains
points, the method returns an
matrix (
being the output dimension).
To make things easier, let us focus on the
case. Let
be the points of firstVertices and let
be the points of secondVertices. The result is the
matrix
such that for any nonnegative integers
and
,
.
- discretize(*args)¶
Discretize the covariance function on a given mesh.
- Parameters:
- where
MeshorRegularGridorSample Container of the discretization vertices
- where
- Returns:
- covarianceMatrix
CovarianceMatrix Covariance matrix
(if the process is of dimension
)
- covarianceMatrix
Notes
This method makes a discretization of the model on the given
Mesh,RegularGridorSamplecomposed of the verticesand returns the covariance matrix:
- discretizeAndFactorize(*args)¶
Discretize and factorize the covariance function on a given mesh.
- Parameters:
- where
MeshorRegularGridorSample Container of the discretization vertices
- where
- Returns:
- CholeskyMatrix
TriangularMatrix Cholesky factor of the covariance matrix
(if the process is of dimension
)
- CholeskyMatrix
Notes
This method makes a discretization of the model on the given
Mesh,RegularGridorSamplecomposed of the verticesthanks to the
discretize()method and returns its Cholesky factor.
- discretizeAndFactorizeHMatrix(*args)¶
Discretize and factorize the covariance function on a given mesh.
This uses HMatrix.
- Parameters:
- where
MeshorRegularGridorSample Container of the discretization vertices
- hmatParam
HMatrixParameters Parameter values for the HMatrix
- where
- Returns:
- HMatrix
HMatrix Cholesk matrix
(if the process is of dimension
), stored in hierarchical format (H-Matrix)
- HMatrix
Notes
This method is similar to the
discretizeAndFactorize()method. This method requires that requires that OpenTURNS has been compiled with the hmat library. The method is helpful for very large parameters (Mesh, grid, Sample) because it compresses data.
- discretizeHMatrix(*args)¶
Discretize the covariance function on a given mesh using HMatrix result.
- Parameters:
- where
MeshorRegularGridorSample Container of the discretization vertices
- hmatParam
HMatrixParameters Parameter values for the HMatrix
- where
- Returns:
- HMatrix
HMatrix Covariance matrix
(if the process is of dimension
), stored in hierarchical format (H-Matrix)
- HMatrix
Notes
This method is similar to the
discretize()method. This method requires that OpenTURNS has been compiled with the hmat library. The method is helpful for very large parameters (Mesh, grid, Sample) because it compresses data.
- discretizeRow(vertices, p)¶
(TODO)
- draw(*args)¶
Not yet implemented
- getActiveLatentVariables()¶
Active latent variables accessor.
- Parameters:
- activeLatentVariables
Point Active coordinates of the categorical levels in the latent space. The inactive coordinates are set to 0 (i.e., the first latent variable is projected onto the Euclidean space origin, and the second latent variable can only be located along the first axis).
- activeLatentVariables
- getActiveParameter()¶
Accessor to the active parameter set.
In the context of kriging, it allows one to choose which hyperparameters are tuned.
- Returns:
- active
Indices Indices of the active parameters.
- active
- getAmplitude()¶
Get the amplitude parameter
of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- amplitude
Point The amplitude parameter
of the covariance function.
- amplitude
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getFullLatentVariables()¶
Latent variables accessor.
- Returns:
- activeLatentVariables
Point Coordinates of the categorical levels in the latent space.
- activeLatentVariables
- getFullParameter()¶
Get the full parameters of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- parameter
Point List of the full parameter of the covariance function i.e. the scale parameter
, the the amplitude parameter
, and the latent variables coordinates,
- parameter
- getFullParameterDescription()¶
Get the description full parameters of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- description
Description Description of the full parameter of the covariance function.
- description
- getInputDimension()¶
Get the input dimension
of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- inputDimensionint
Spatial dimension
of the covariance function.
- getLatentDimension()¶
Latent dimension accessor.
- Returns:
- latentDimensionint
Dimension of the latent space.
- getLevelNumber()¶
Level number accessor.
- Returns:
- nLevelsint
Number of levels
characterizing the categorical variable.
- getMarginal(*args)¶
Get the ith marginal of the model.
- Returns:
- marginalint or sequence of int
index of marginal of the model.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getNuggetFactor()¶
Accessor to the nugget factor.
This parameter allows smooth predictions from noisy data. The nugget is added to the diagonal of the assumed training covariance (thanks to discretize) and acts as a Tikhonov regularization in the problem.
- Returns:
- nuggetFactorfloat
Nugget factor used to model the observation error variance.
- getOutputCorrelation()¶
Get the spatial correlation matrix
of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- spatialCorrelation
CorrelationMatrix Correlation matrix
.
- spatialCorrelation
- getOutputDimension()¶
Get the dimension
of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- dint
Dimension
such that
This is the dimension of the process
.
- getParameter()¶
Get the parameters of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- parameters
Point List of the scale parameter
and the amplitude parameter
of the covariance function.
The other specific parameters are not included.
- parameters
- getParameterDescription()¶
Get the description of the covariance function parameters.
- Returns:
- descriptionParam
Description Description of the components of the parameters obtained with the getParameter method..
- descriptionParam
- getScale()¶
Get the scale parameter
of the covariance function.
- Returns:
- scale
Point The scale parameter
used in the covariance function.
- scale
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- isDiagonal()¶
Test whether the model is diagonal or not.
- Returns:
- isDiagonalbool
True if the model is diagonal.
- isStationary()¶
Test whether the model is stationary or not.
- Returns:
- isStationarybool
True if the model is stationary.
Notes
The covariance function
is stationary when it is invariant by translation:
We note
for
.
- parameterGradient(s, t)¶
Compute the gradient according to the parameters.
- Parameters:
- s, tsequences of float
Multivariate index
.
- Returns:
- gradient
Matrix Gradient of the function according to the parameters.
- gradient
- partialGradient(s, t)¶
Compute the gradient of the covariance function.
- Parameters:
- s, tfloats or sequences of float
Multivariate index
.
- Returns:
- gradient
Matrix Gradient of the covariance function.
- gradient
- setActiveParameter(active)¶
Accessor to the active parameter set.
In the context of kriging, it allows one to choose which hyperparameters are tuned.
- Parameters:
- activesequence of int
Indices of the active parameters.
- setAmplitude(amplitude)¶
Set the amplitude parameter
of the covariance function.
- Parameters:
- amplitude
Point The amplitude parameter
to be used in the covariance function. Its size must be equal to the dimension of the covariance function.
- amplitude
- setFullParameter(parameter)¶
Set the full parameters of the covariance function.
- Parameters:
- parameter
Point List of the full parameter of the covariance function i.e. the scale parameter
, the the amplitude parameter
, and the latent variables coordinates,
- parameter
- setLatentVariables(latentVariablesCoordinates)¶
Number of levels accessor.
- Parameters:
- LatentVariablessequence of float
Active coordinates of the categorical levels in the latent space.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setNuggetFactor(nuggetFactor)¶
Set the nugget factor for the variance of the observation error.
Acts on the discretized covariance matrix.
- Parameters:
- nuggetFactorfloat
nugget factor to be used to model the variance of the observation error.
- setOutputCorrelation(correlation)¶
Set the spatial correlation matrix
of the covariance function.
- Parameters:
- spatialCorrelation
CorrelationMatrix Correlation matrix
.
- spatialCorrelation
Examples using the class¶
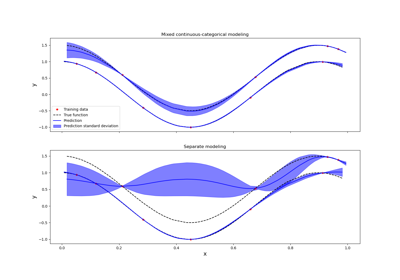
Kriging: metamodel with continuous and categorical variables
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS