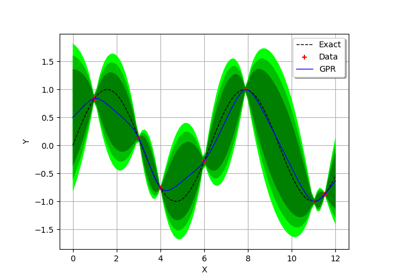
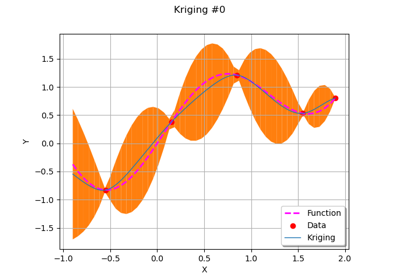
GaussianProcessRegressionResult¶
- class GaussianProcessRegressionResult(*args)¶
Gaussian process regression (aka kriging) result.
Warning
This class is experimental and likely to be modified in future releases. To use it, import the
openturns.experimentalsubmodule.- Parameters:
- gpfResult
GaussianProcessFitterResult Structure result of a gaussian process fitter.
- covarianceCoefficients2-d sequence of float
The
defined in (2).
- gpfResult
Methods
getBasis()Accessor to the collection of basis.
Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the covariance coefficients.
Accessor to the covariance model.
Accessor to the input sample.
Accessor to the used linear algebra method to fit.
Accessor to the metamodel.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
getNoise()Accessor to the Gaussian process.
Accessor to the optimal log-likelihood of the model.
Accessor to the output sample.
Accessor to the regression matrix.
Accessor to the relative errors.
Accessor to the residuals.
Accessor to the trend coefficients.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
setInputSample(sampleX)Accessor to the input sample.
setMetaModel(metaModel)Accessor to the metamodel.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setOutputSample(sampleY)Accessor to the output sample.
setRelativeErrors(relativeErrors)Accessor to the relative errors.
setResiduals(residuals)Accessor to the residuals.
Notes
The Gaussian Process Regression (aka Kriging) meta model
is defined by:
(1)¶
where
is the condition
for each
.
Equation (1) writes:
where
and
(2)¶
At the end, the meta model writes:
(3)¶
Examples
Create the model
and the samples:
>>> import openturns as ot >>> import openturns.experimental as otexp >>> g = ot.SymbolicFunction(['x'], ['x * sin(x)']) >>> sampleX = [[1.0], [2.0], [3.0], [4.0], [5.0], [6.0]] >>> sampleY = g(sampleX)
Create the algorithm:
>>> basis = ot.Basis([ot.SymbolicFunction(['x'], ['x']), ot.SymbolicFunction(['x'], ['x^2'])]) >>> covarianceModel = ot.GeneralizedExponential([2.0], 2.0)
>>> fit_algo = otexp.GaussianProcessFitter(sampleX, sampleY, covarianceModel, basis) >>> fit_algo.run()
>>> algo = otexp.GaussianProcessRegression(fit_algo.getResult()) >>> algo.run()
Get the result:
>>> result = algo.getResult()
Get the meta model:
>>> metaModel = result.getMetaModel()
- __init__(*args)¶
- getBasis()¶
Accessor to the collection of basis.
- Returns:
- basis
Basis Functional basis of size
:
for each
.
- basis
Notes
If the trend is not estimated, the basis is empty.
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getCovarianceCoefficients()¶
Accessor to the covariance coefficients.
- getCovarianceModel()¶
Accessor to the covariance model.
- Returns:
- covModel
CovarianceModel The covariance model of the Gaussian process W.
- covModel
- getLinearAlgebraMethod()¶
Accessor to the used linear algebra method to fit.
- Returns:
- linAlgMethodint
The used linear algebra method to fit the model:
otexp.GaussianProcessFitterResult.LAPACK or 0: using LAPACK to fit the model,
otexp.GaussianProcessFitterResult.HMAT or 1: using HMAT to fit the model.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getNoise()¶
Accessor to the Gaussian process.
- Returns:
- process
Process Returns the Gaussian process
with the optimized parameters.
- process
- getOptimalLogLikelihood()¶
Accessor to the optimal log-likelihood of the model.
- Returns:
- optimalLogLikelihoodfloat
The value of the log-likelihood corresponding to the model.
- getRegressionMatrix()¶
Accessor to the regression matrix.
- Returns:
- process
Matrix Returns the regression matrix.
- process
- getRelativeErrors()¶
Accessor to the relative errors.
- Returns:
- relativeErrors
Point The relative errors defined as follows for each output of the model:
with
the vector of the
model’s values
and
the metamodel’s values.
- relativeErrors
- getResiduals()¶
Accessor to the residuals.
- Returns:
- residuals
Point The residual values defined as follows for each output of the model:
with
the
model’s values and
the metamodel’s values.
- residuals
- getTrendCoefficients()¶
Accessor to the trend coefficients.
- Returns:
- trendCoefsequence of float
The trend coefficients vectors
as a
Point
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- setInputSample(sampleX)¶
Accessor to the input sample.
- Parameters:
- inputSample
Sample The input sample.
- inputSample
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setOutputSample(sampleY)¶
Accessor to the output sample.
- Parameters:
- outputSample
Sample The output sample.
- outputSample
- setRelativeErrors(relativeErrors)¶
Accessor to the relative errors.
- Parameters:
- relativeErrorssequence of float
The relative errors defined as follows for each output of the model:
with
the vector of the
model’s values
and
the metamodel’s values.
- setResiduals(residuals)¶
Accessor to the residuals.
- Parameters:
- residualssequence of float
The residual values defined as follows for each output of the model:
with
the
model’s values and
the metamodel’s values.
Examples using the class¶
Gaussian Process Regression : cantilever beam model
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS