Note
Click here to download the full example code
Create a gaussian process from a cov. model¶
In this example we are going to build a gaussian process from its covariance model.
from __future__ import print_function
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
define a covariance model
defaultDimension = 1
# Amplitude values
amplitude = [1.0]*defaultDimension
# Scale values
scale = [1.0]*defaultDimension
# Covariance model
myModel = ot.AbsoluteExponential(scale, amplitude)
define a mesh
tmin = 0.0
step = 0.1
n = 11
myTimeGrid = ot.RegularGrid(tmin, step, n)
create the process
process = ot.GaussianProcess(myModel, myTimeGrid)
print(process)
Out:
GaussianProcess(trend=[x0]->[0.0], covariance=AbsoluteExponential(scale=[1], amplitude=[1]))
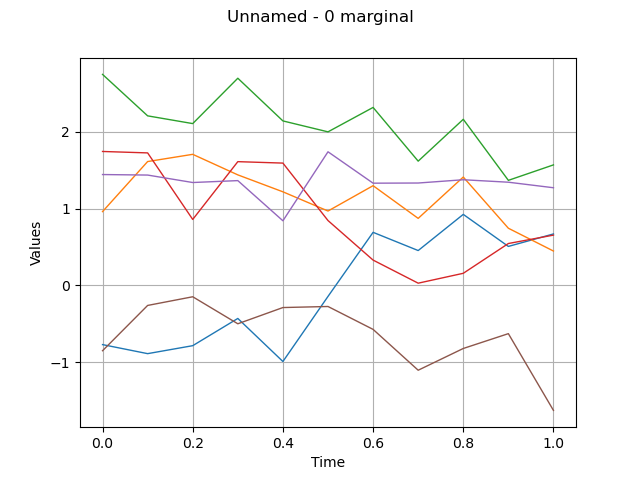
draw a sample
sample = process.getSample(6)
graph = sample.drawMarginal(0)
view = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.069 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS