Note
Click here to download the full example code
Distribution manipulation¶
In this example we are going to exhibit some of the services exposed by the distribution objects:
ask for the dimension, with the method getDimension
extract the marginal distributions, with the method getMarginal
to ask for some properties, with isContinuous, isDiscrete, isElliptical
to get the copula, with the method getCopula*
to ask for some properties on the copula, with the methods hasIndependentCopula, hasEllipticalCopula
to evaluate some moments, with getMean, getStandardDeviation, getCovariance, getSkewness, getKurtosis
to evaluate the roughness, with the method getRoughness
to get one realization or simultaneously
realizations, with the method getRealization, getSample
to evaluate the probability content of a given interval, with the method computeProbability
to evaluate a quantile or a complementary quantile, with the method computeQuantile
to evaluate the characteristic function of the distribution
to evaluate the derivative of the CDF or PDF
to draw some curves
from __future__ import print_function
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
Create an 1-d distribution
dist_1 = ot.Normal()
# Create a 2-d distribution
dist_2 = ot.ComposedDistribution([ot.Normal(), ot.Triangular(0.0, 2.0, 3.0)], ot.ClaytonCopula(2.3))
# Create a 3-d distribution
copula_dim3 = ot.Student(5.0, 3).getCopula()
dist_3 = ot.ComposedDistribution([ot.Normal(), ot.Triangular(0.0, 2.0, 3.0), ot.Exponential(0.2)], copula_dim3)
Get the dimension fo the distribution
dist_2.getDimension()
Out:
2
Get the 2nd marginal
dist_2.getMarginal(1)
Get a 2-d marginal
dist_3.getMarginal([0, 1]).getDimension()
Out:
2
Ask some properties of the distribution
dist_1.isContinuous(), dist_1.isDiscrete(), dist_1.isElliptical()
Out:
(True, False, True)
Get the copula
copula = dist_2.getCopula()
Ask some properties on the copula
dist_2.hasIndependentCopula(), dist_2.hasEllipticalCopula()
Out:
(False, False)
mean vector of the distribution
dist_2.getMean()
standard deviation vector of the distribution
dist_2.getStandardDeviation()
covariance matrix of the distribution
dist_2.getCovariance()
skewness vector of the distribution
dist_2.getSkewness()
kurtosis vector of the distribution
dist_2.getKurtosis()
roughness of the distribution
dist_1.getRoughness()
Out:
0.28209479177387814
Get one realization
dist_2.getRealization()
Get several realizations
dist_2.getSample(5)
Evaluate the PDF at the mean point
dist_2.computePDF(dist_2.getMean())
Out:
0.3528005531670077
Evaluate the CDF at the mean point
dist_2.computeCDF(dist_2.getMean())
Out:
0.3706626446357781
Evaluate the complementary CDF
dist_2.computeComplementaryCDF(dist_2.getMean())
Out:
0.6293373553642219
Evaluate the survival function at the mean point
dist_2.computeSurvivalFunction(dist_2.getMean())
Out:
0.4076996816728151
Evaluate the PDF on a sample
dist_2.computePDF(dist_2.getSample(5))
Evaluate the CDF on a sample
dist_2.computeCDF(dist_2.getSample(5))
Evaluate the probability content of an 1-d interval
interval = ot.Interval(-2.0, 3.0)
dist_1.computeProbability(interval)
Out:
0.9758999700201907
Evaluate the probability content of a 2-d interval
interval = ot.Interval([0.4, -1], [3.4, 2])
dist_2.computeProbability(interval)
Out:
0.129833882783416
Evaluate the quantile of order p=90%
dist_2.computeQuantile(0.90)
and the quantile of order 1-p
dist_2.computeQuantile(0.90, True)
Evaluate the quantiles of order p et q For example, the quantile 90% and 95%
dist_1.computeQuantile([0.90, 0.95])
and the quantile of order 1-p and 1-q
dist_1.computeQuantile([0.90, 0.95], True)
Evaluate the characteristic function of the distribution (only 1-d)
dist_1.computeCharacteristicFunction(dist_1.getMean()[0])
Out:
(1+0j)
Evaluate the derivatives of the PDF with respect to the parameters at mean
dist_2.computePDFGradient(dist_2.getMean())
Evaluate the derivatives of the CDF with respect to the parameters at mean
dist_2.computeCDFGradient(dist_2.getMean())
draw PDF
graph = dist_1.drawPDF()
view = viewer.View(graph)
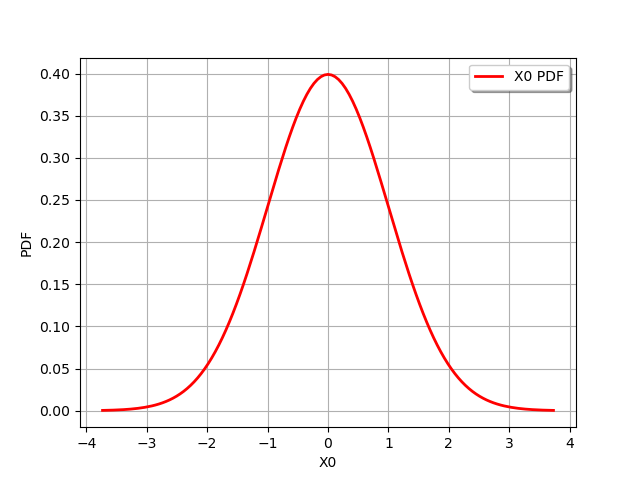
draw CDF
graph = dist_1.drawCDF()
view = viewer.View(graph)
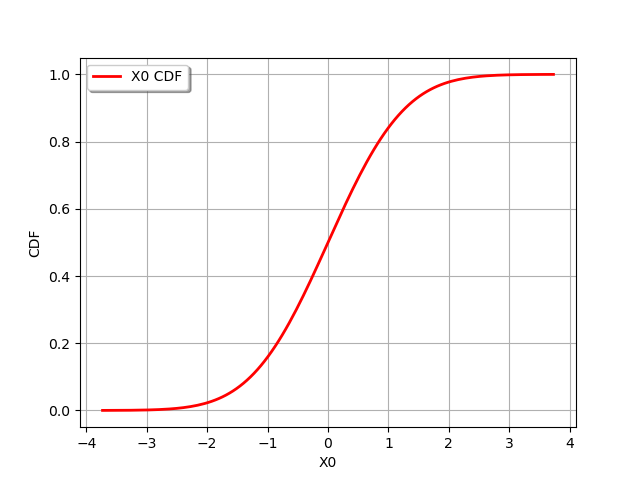
Draw an 1-d quantile curve
# Define the range and the number of points
qMin = 0.2
qMax = 0.6
nbrPoints = 101
quantileGraph = dist_1.drawQuantile(qMin, qMax, nbrPoints)
view = viewer.View(quantileGraph)
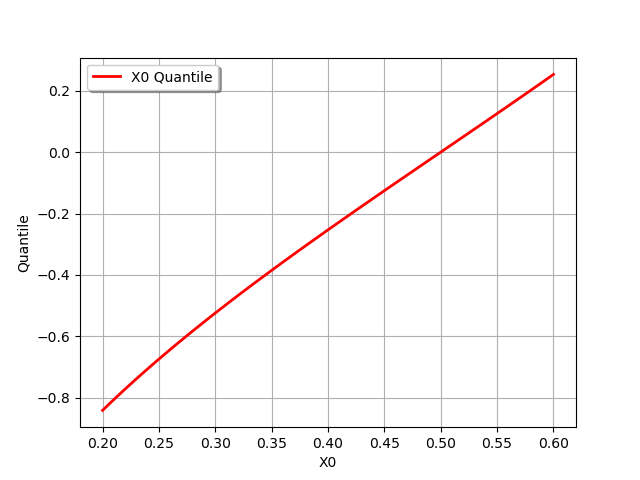
Draw a 2-d quantile curve
# Define the range and the number of points
qMin = 0.3
qMax = 0.9
nbrPoints = 101
quantileGraph = dist_2.drawQuantile(qMin, qMax, nbrPoints)
view = viewer.View(quantileGraph)
plt.show()
![[X0,X1] Quantile](../../_images/sphx_glr_plot_distribution_manipulation_004.png)
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.806 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS