Note
Click here to download the full example code
Sobol’ sensitivity indices from chaos¶
In this example we are going to compute global sensitivity indices from a functional chaos decomposition.
We study the Borehole function that models water flow through a borehole:
With parameters:
: radius of borehole (m)
: radius of influence (m)
: transmissivity of upper aquifer (
)
: potentiometric head of upper aquifer (m)
: transmissivity of lower aquifer (
)
: potentiometric head of lower aquifer (m)
: length of borehole (m)
: hydraulic conductivity of borehole (
)
from __future__ import print_function
import openturns as ot
from operator import itemgetter
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
borehole model
dimension = 8
input_names = ['rw', 'r', 'Tu', 'Hu', 'Tl', 'Hl', 'L', 'Kw']
model = ot.SymbolicFunction(input_names,
['(2*pi_*Tu*(Hu-Hl))/(ln(r/rw)*(1+(2*L*Tu)/(ln(r/rw)*rw^2*Kw)+Tu/Tl))'])
coll = [ot.Normal(0.1, 0.0161812),
ot.LogNormal(7.71, 1.0056),
ot.Uniform(63070.0, 115600.0),
ot.Uniform(990.0, 1110.0),
ot.Uniform(63.1, 116.0),
ot.Uniform(700.0, 820.0),
ot.Uniform(1120.0, 1680.0),
ot.Uniform(9855.0, 12045.0)]
distribution = ot.ComposedDistribution(coll)
distribution.setDescription(input_names)
Freeze r, Tu, Tl from model to go faster
selection = [1, 2, 4]
complement = ot.Indices(selection).complement(dimension)
distribution = distribution.getMarginal(complement)
model = ot.ParametricFunction(
model, selection, distribution.getMarginal(selection).getMean())
input_names_copy = list(input_names)
input_names = itemgetter(*complement)(input_names)
dimension = len(complement)
design of experiment
size = 1000
X = distribution.getSample(size)
Y = model(X)
create a functional chaos model
algo = ot.FunctionalChaosAlgorithm(X, Y)
algo.run()
result = algo.getResult()
print(result.getResiduals())
print(result.getRelativeErrors())
Out:
[0.00472648]
[4.13378e-08]
Quick summary of sensitivity analysis
sensitivityAnalysis = ot.FunctionalChaosSobolIndices(result)
print(sensitivityAnalysis.summary())
Out:
input dimension: 5
output dimension: 1
basis size: 56
mean: [74.8252]
std-dev: [28.86]
------------------------------------------------------------
Index | Multi-indice | Part of variance
------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [1,0,0,0,0] | 0.667533
3 | [0,0,1,0,0] | 0.0972783
4 | [0,0,0,1,0] | 0.0906816
2 | [0,1,0,0,0] | 0.0798009
5 | [0,0,0,0,1] | 0.0221444
------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------
Component | Sobol index | Sobol total index
------------------------------------------------------------
0 | 0.67653 | 0.705682
1 | 0.0798379 | 0.0891789
2 | 0.0972796 | 0.108678
3 | 0.0916856 | 0.103876
4 | 0.0221444 | 0.0254584
------------------------------------------------------------
draw Sobol’ indices
first_order = [sensitivityAnalysis.getSobolIndex(i) for i in range(dimension)]
total_order = [sensitivityAnalysis.getSobolTotalIndex(
i) for i in range(dimension)]
graph = ot.SobolIndicesAlgorithm.DrawSobolIndices(
input_names, first_order, total_order)
view = viewer.View(graph)
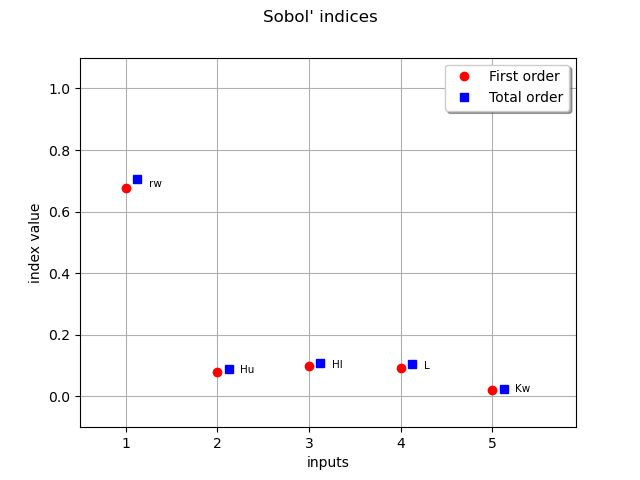
We saw that total order indices are close to first order, so the higher order indices must be all quite close to 0
for i in range(dimension):
for j in range(i):
print(input_names[i] + ' & ' + input_names[j], ":",
sensitivityAnalysis.getSobolIndex([i, j]))
plt.show()
Out:
Hu & rw : 0.007773952603684
Hl & rw : 0.009536145155773607
Hl & Hu : 5.4681169248072785e-05
L & rw : 0.00917958869007991
L & Hu : 0.0010928197895924347
L & Hl : 0.001315360782351903
Kw & rw : 0.002320368250935267
Kw & Hu : 0.00027291064768849286
Kw & Hl : 0.00031801092178630964
Kw & L : 0.0003073000271333149
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 2.739 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS