Note
Click here to download the full example code
Calibration of the deflection of a tube¶
We calibrate the deflection of a tube as described here. More precisely, we calibrate the mechanical parameters of a model which computes the vertical deflection of a tube and two deflection angles. This example shows how to calibrate a computer code which has several outputs.
from openturns.usecases import deflection_tube
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
Create a calibration problem¶
We load the model from the use case module :
dt = deflection_tube.DeflectionTube()
We create a sample out of our input distribution :
sampleSize = 100
inputSample = dt.inputDistribution.getSample(sampleSize)
inputSample[0:5]
We take the image of our input sample by the model :
outputDeflection = dt.model(inputSample)
outputDeflection[0:5]
observationNoiseSigma = [0.1e-6, 0.05e-5, 0.05e-5]
observationNoiseCovariance = ot.CovarianceMatrix(3)
for i in range(3):
observationNoiseCovariance[i, i] = observationNoiseSigma[i]**2
noiseSigma = ot.Normal([0., 0., 0.], observationNoiseCovariance)
sampleObservationNoise = noiseSigma.getSample(sampleSize)
observedOutput = outputDeflection + sampleObservationNoise
observedOutput[0:5]
observedInput = ot.Sample(sampleSize, 2)
observedInput[:, 0] = inputSample[:, 0] # F
observedInput[:, 1] = inputSample[:, 5] # E
observedInput.setDescription(["Force", "Young Modulus"])
observedInput[0:5]
fullSample = ot.Sample(sampleSize, 5)
fullSample[:, 0:2] = observedInput
fullSample[:, 2:5] = observedOutput
fullSample.setDescription(
["Force", "Young", "Deflection", "Left Angle", "Right Angle"])
fullSample[0:5]
graph = ot.VisualTest.DrawPairs(fullSample)
view = viewer.View(graph)
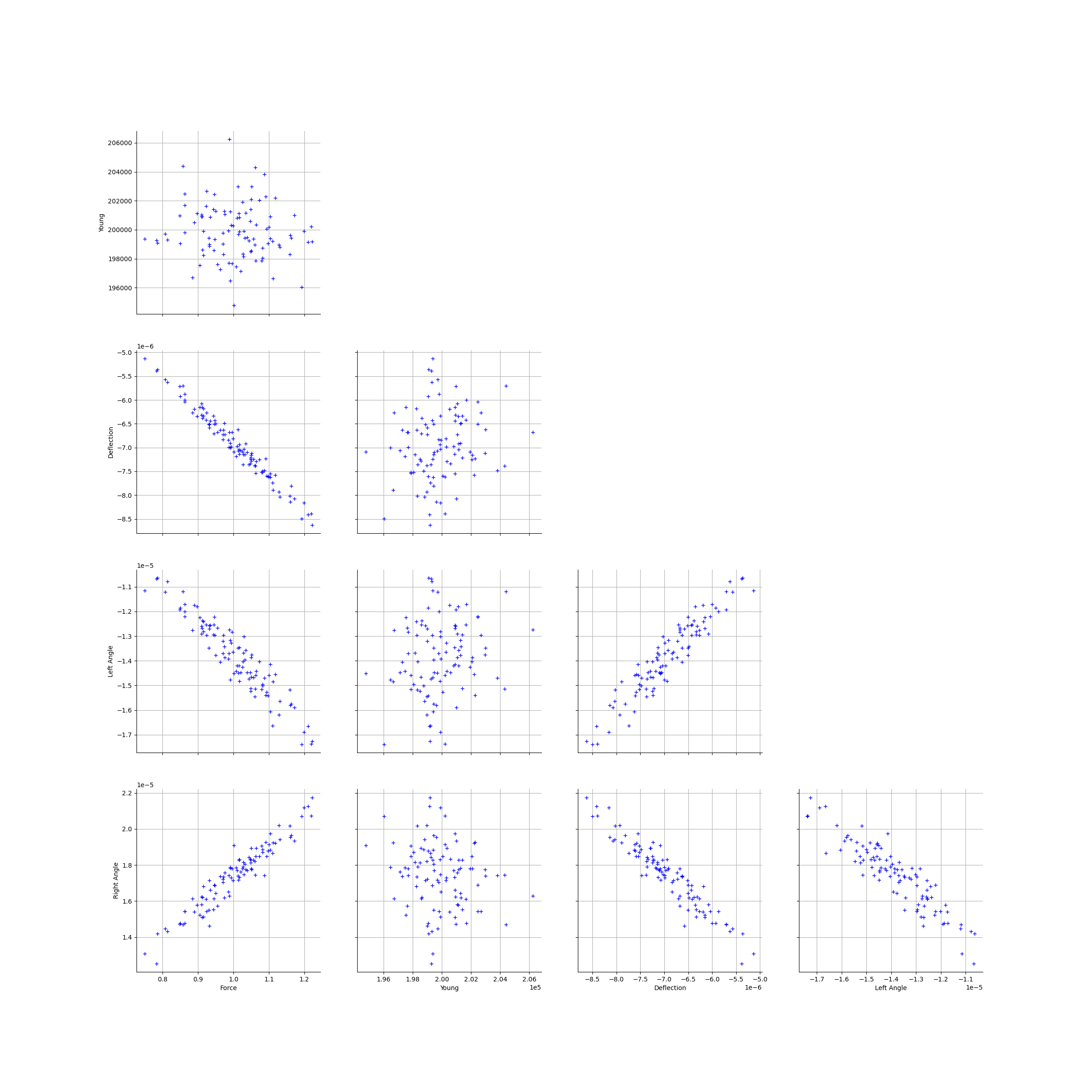
Setting up the calibration¶
XL = 1.4 # Exact : 1.5
Xa = 1.2 # Exact : 1.0
XD = 0.7 # Exact : 0.8
Xd = 0.2 # Exact : 0.1
thetaPrior = [XL, Xa, XD, Xd]
sigmaXL = 0.1 * XL
sigmaXa = 0.1 * Xa
sigmaXD = 0.1 * XD
sigmaXd = 0.1 * Xd
parameterCovariance = ot.CovarianceMatrix(4)
parameterCovariance[0, 0] = sigmaXL**2
parameterCovariance[1, 1] = sigmaXa**2
parameterCovariance[2, 2] = sigmaXD**2
parameterCovariance[3, 3] = sigmaXd**2
parameterCovariance
calibratedIndices = [1, 2, 3, 4]
calibrationFunction = ot.ParametricFunction(
dt.model, calibratedIndices, thetaPrior)
sigmaObservation = [0.2e-6, 0.03e-5, 0.03e-5] # Exact : 0.1e-6
errorCovariance = ot.CovarianceMatrix(3)
errorCovariance[0, 0] = sigmaObservation[0]**2
errorCovariance[1, 1] = sigmaObservation[1]**2
errorCovariance[2, 2] = sigmaObservation[2]**2
calibrationFunction.setParameter(thetaPrior)
predictedOutput = calibrationFunction(observedInput)
predictedOutput[0:5]
Calibration with gaussian non linear least squares¶
algo = ot.GaussianNonLinearCalibration(
calibrationFunction, observedInput, observedOutput, thetaPrior, parameterCovariance, errorCovariance)
algo.run()
calibrationResult = algo.getResult()
Analysis of the results¶
thetaMAP = calibrationResult.getParameterMAP()
thetaMAP
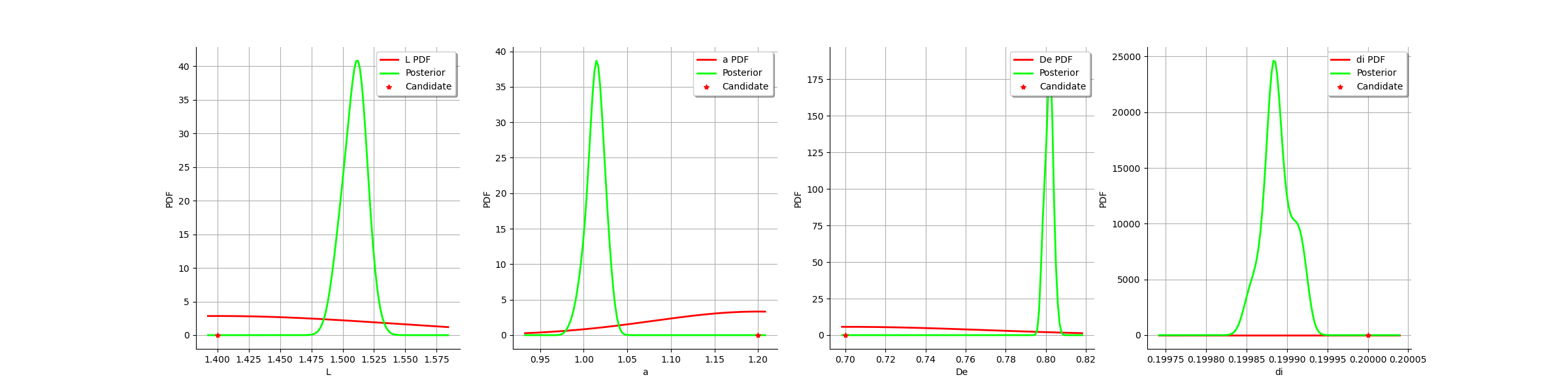
Compute a 95% confidence interval for each marginal.
thetaPosterior = calibrationResult.getParameterPosterior()
alpha = 0.95
dim = thetaPosterior.getDimension()
for i in range(dim):
print(thetaPosterior.getMarginal(i).computeBilateralConfidenceInterval(alpha))
Out:
[1.48921, 1.52789]
[0.990035, 1.03407]
[0.797322, 0.80576]
[0.19985, 0.199926]
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsInputs()
view = viewer.View(graph)
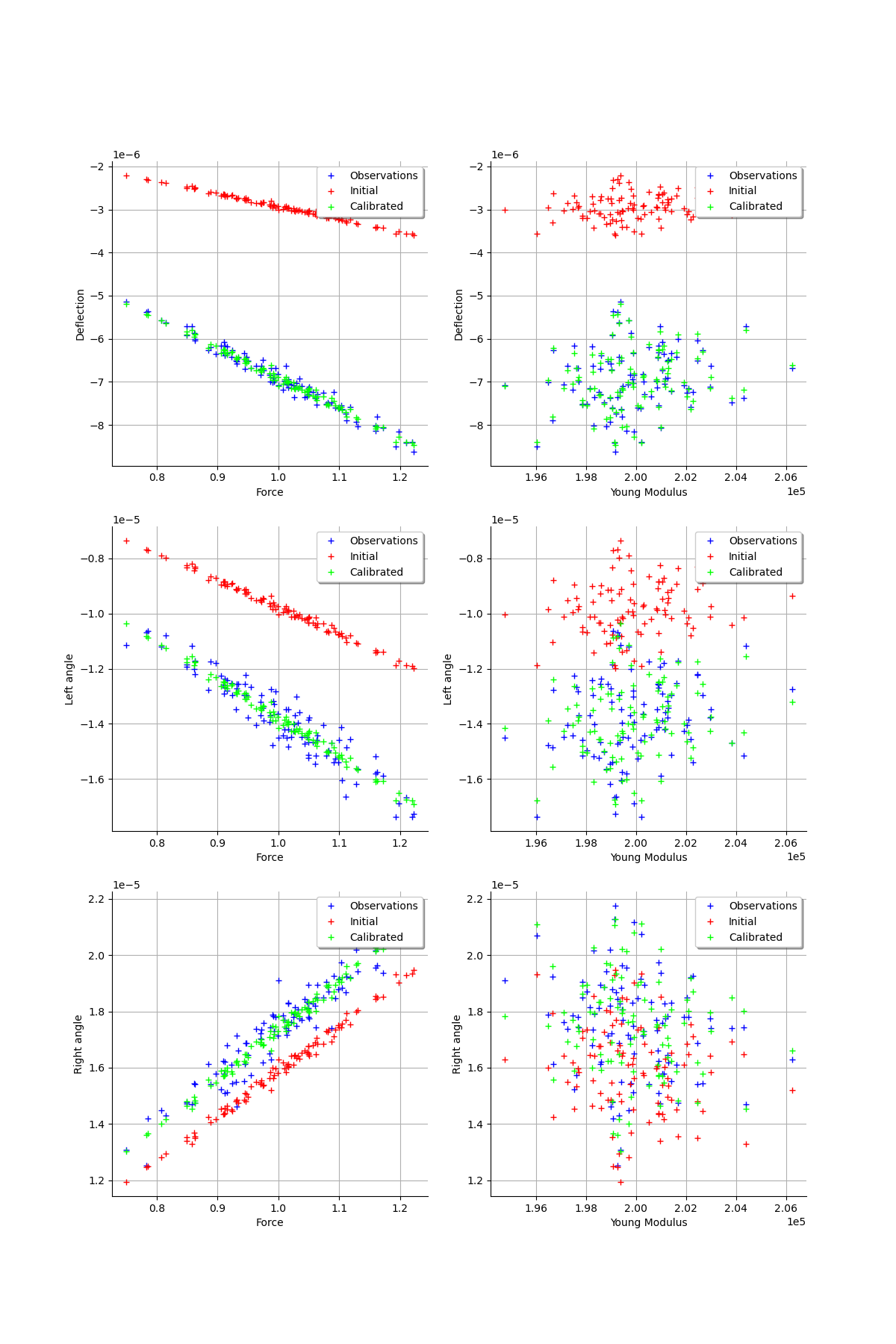
graph = calibrationResult.drawObservationsVsPredictions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
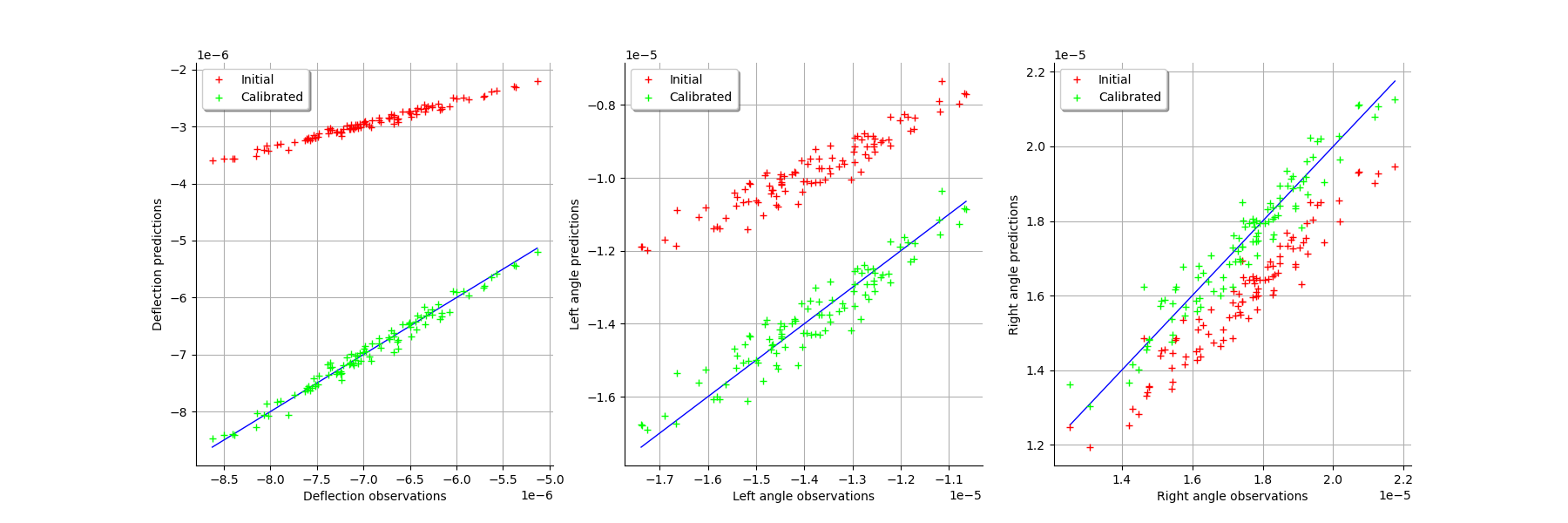
graph = calibrationResult.drawResiduals()
view = viewer.View(graph)
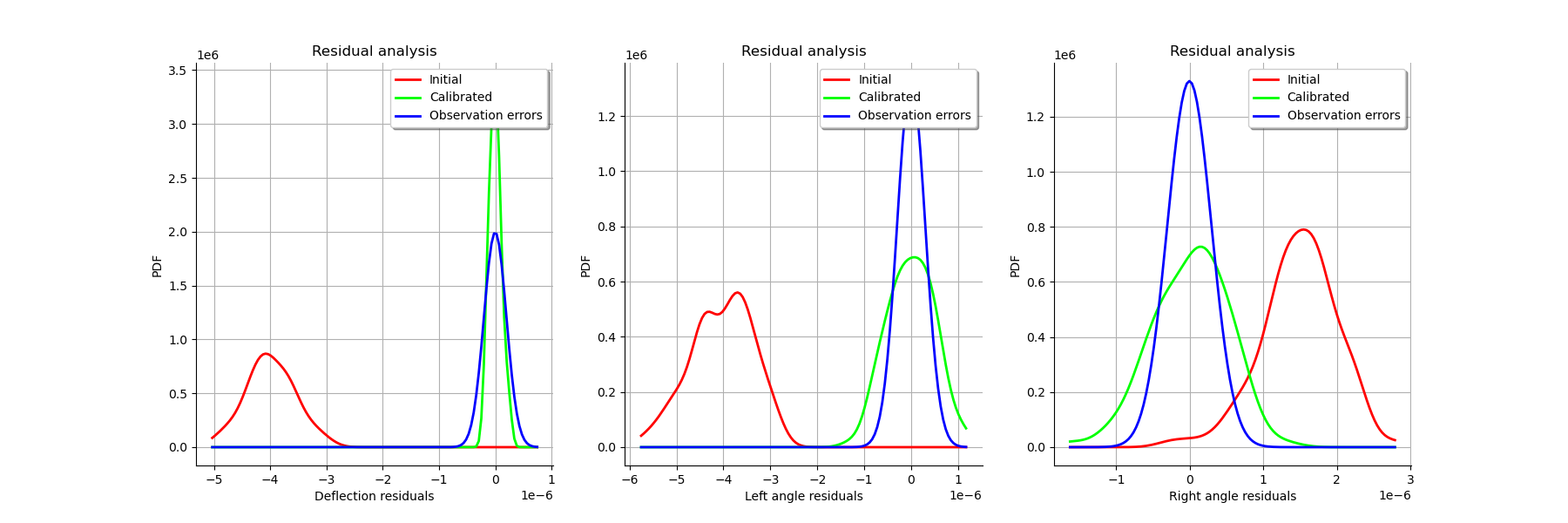
graph = calibrationResult.drawParameterDistributions()
view = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 4.204 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS