Note
Click here to download the full example code
Kolmogorov-Smirnov : get the statistics distribution¶
- In this example, we draw the Kolmogorov-Smirnov distribution for a sample size 10.
We want to test the hypothesis that this sample has the Uniform(0, 1) distribution. The K.S. distribution is first plotted in the case where the
- parameters of the uniform distribution are known.
Then we plot the distribution when the parameters of the uniform distribution are estimated from the sample.
Reference : Hovhannes Keutelian, “The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test when parameters are estimated from data”, 30 April 1991, Fermilab
Note: There is a sign error in the paper; the equation: D[i]=max(abs(S+step),D[i]) must be replaced with D[i]=max(abs(S-step),D[i]).
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
x = [0.9374, 0.7629, 0.4771, 0.5111, 0.8701,
0.0684, 0.7375, 0.5615, 0.2835, 0.2508]
sample = ot.Sample([[xi] for xi in x])
samplesize = sample.getSize()
samplesize
Out:
10
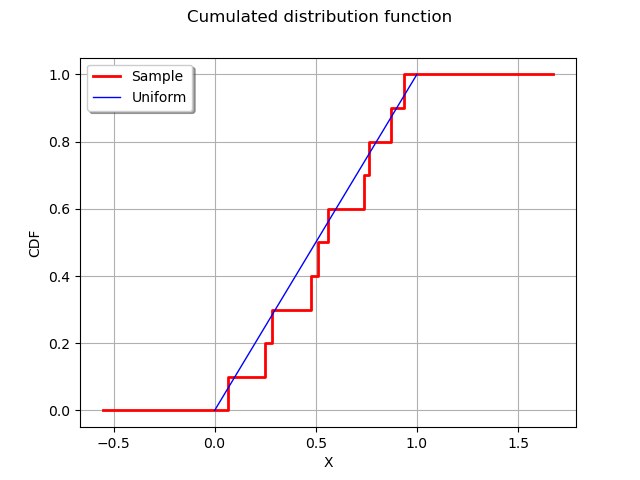
Plot the empirical distribution function.
graph = ot.UserDefined(sample).drawCDF()
graph.setLegends(["Sample"])
curve = ot.Curve([0, 1], [0, 1])
curve.setLegend("Uniform")
graph.add(curve)
graph.setXTitle("X")
graph.setTitle("Cumulated distribution function")
view = viewer.View(graph)
The computeKSStatisticsIndex function computes the Kolmogorov-Smirnov distance between the sample and the distribution. The following function is for teaching purposes only: use FittingTest for real applications.
def computeKSStatistics(sample, distribution):
sample = sample.sort()
n = sample.getSize()
D = 0.
index = -1
D_previous = 0.
for i in range(n):
F = distribution.computeCDF(sample[i])
Fminus = F - float(i)/n
Fplus = float(i+1)/n - F
D = max(Fminus, Fplus, D)
if (D > D_previous):
index = i
D_previous = D
return D
dist = ot.Uniform(0, 1)
dist
computeKSStatistics(sample, dist)
Out:
0.17710000000000004
The following function generates a sample of K.S. distances when the tested distribution is the Uniform(0,1) distribution.
def generateKSSampleKnownParameters(nrepeat, samplesize):
"""
nrepeat : Number of repetitions, size of the table
samplesize : the size of each sample to generate from the Uniform distribution
"""
dist = ot.Uniform(0, 1)
D = ot.Sample(nrepeat, 1)
for i in range(nrepeat):
sample = dist.getSample(samplesize)
D[i, 0] = computeKSStatistics(sample, dist)
return D
Generate a sample of KS distances.
nrepeat = 10000 # Size of the KS distances sample
sampleD = generateKSSampleKnownParameters(nrepeat, samplesize)
Compute exact Kolmogorov CDF.
def pKolmogorovPy(x):
y = ot.DistFunc.pKolmogorov(samplesize, x[0])
return [y]
pKolmogorov = ot.PythonFunction(1, 1, pKolmogorovPy)
def dKolmogorov(x, samplesize):
"""
Compute Kolmogorov PDF for given x.
x : an array, the points where the PDF must be evaluated
samplesize : the size of the sample
Reference
Numerical Derivatives in Scilab, Michael Baudin, May 2009
"""
n = x.getSize()
y = ot.Sample(n, 1)
for i in range(n):
y[i, 0] = pKolmogorov.gradient(x[i])[0, 0]
return y
def linearSample(xmin, xmax, npoints):
'''Returns a sample created from a regular grid
from xmin to xmax with npoints points.'''
step = (xmax-xmin)/(npoints-1)
rg = ot.RegularGrid(xmin, step, npoints)
vertices = rg.getVertices()
return vertices
n = 1000 # Number of points in the plot
s = linearSample(0.001, 0.999, n)
y = dKolmogorov(s, samplesize)
curve = ot.Curve(s, y)
curve.setLegend("Exact distribution")
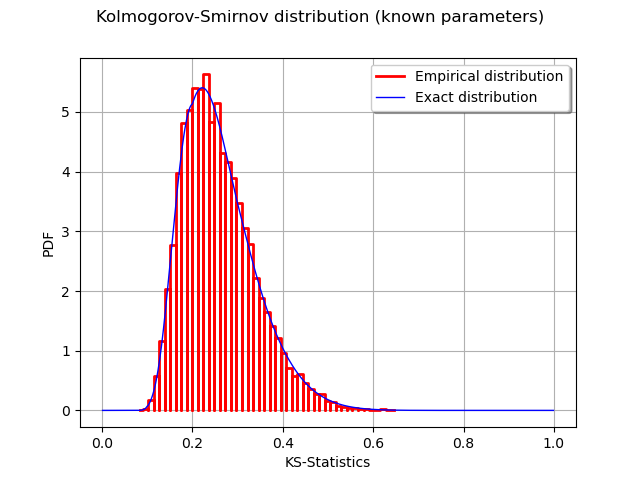
graph = ot.HistogramFactory().build(sampleD).drawPDF()
graph.setLegends(["Empirical distribution"])
graph.add(curve)
graph.setTitle("Kolmogorov-Smirnov distribution (known parameters)")
graph.setXTitle("KS-Statistics")
view = viewer.View(graph)
Known parameters versus estimated parameters¶
The following function generates a sample of K.S. distances when the tested distribution is the Uniform(a,b) distribution, where the a and b parameters are estimated from the sample.
def generateKSSampleEstimatedParameters(nrepeat, samplesize):
"""
nrepeat : Number of repetitions, size of the table
samplesize : the size of each sample to generate from the Uniform distribution
"""
distfactory = ot.UniformFactory()
refdist = ot.Uniform(0, 1)
D = ot.Sample(nrepeat, 1)
for i in range(nrepeat):
sample = refdist.getSample(samplesize)
trialdist = distfactory.build(sample)
D[i, 0] = computeKSStatistics(sample, trialdist)
return D
Generate a sample of KS distances.
sampleDP = generateKSSampleEstimatedParameters(nrepeat, samplesize)
graph = ot.KernelSmoothing().build(sampleD).drawPDF()
graph.setLegends(["Known parameters"])
graphP = ot.KernelSmoothing().build(sampleDP).drawPDF()
graphP.setLegends(["Estimated parameters"])
graphP.setColors(["blue"])
graph.add(graphP)
graph.setTitle("Kolmogorov-Smirnov distribution")
graph.setXTitle("KS-Statistics")
view = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
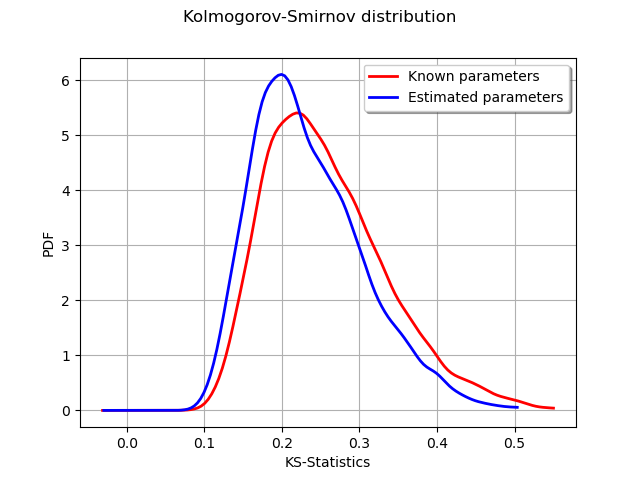
We see that the distribution of the KS distances when the parameters are estimated is shifted towards the left: smaller distances occur more often. This is a consequence of the fact that the estimated parameters tend to make the estimated distribution closer to the empirical sample.
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 1.010 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS