Note
Click here to download the full example code
Taylor approximations¶
In this example we are going to build a local approximation of a model using the Taylor decomposition:
Here is the decomposition at the first order:
Here .
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
# Prepare some data.
formulas = ['cos(x1 + x2)', '(x2 + 1) * exp(x1 - 2 * x2)']
model = ot.SymbolicFunction(['x1', 'x2'], formulas)
# Center of the approximation.
x0 = [-0.4, -0.4]
# Drawing bounds.
a = -0.4
b = 0.0
Create a linear (first-order) Taylor approximation.
algo = ot.LinearTaylor(x0, model)
algo.run()
responseSurface = algo.getMetaModel()
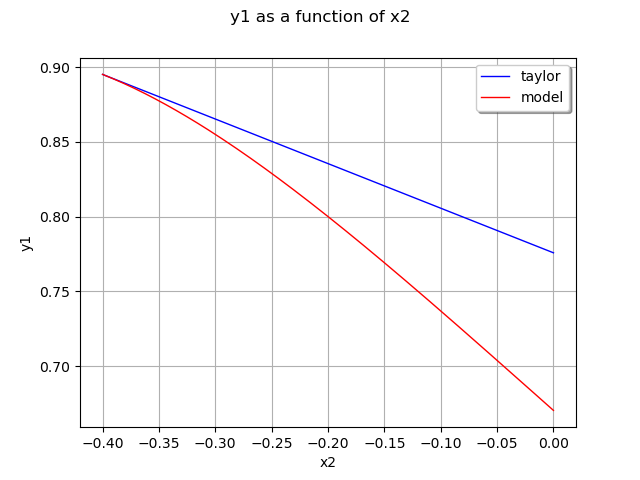
Plot the second output of our model with .
graph = ot.ParametricFunction(
responseSurface, [0], [x0[1]]).getMarginal(1).draw(a, b)
graph.setLegends(['taylor'])
curve = ot.ParametricFunction(model, [0], [x0[1]]).getMarginal(
1).draw(a, b).getDrawable(0)
curve.setColor('red')
curve.setLegend('model')
graph.add(curve)
graph.setLegendPosition('topright')
view = viewer.View(graph)
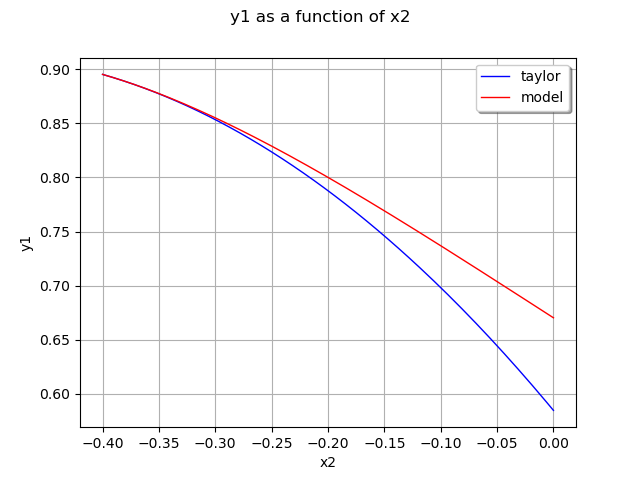
Here is the decomposition at the second order:
Create a quadratic (second-order) Taylor approximation.
algo = ot.QuadraticTaylor(x0, model)
algo.run()
responseSurface = algo.getMetaModel()
Plot second output of our model with .
graph = ot.ParametricFunction(
responseSurface, [0], [x0[1]]).getMarginal(1).draw(a, b)
graph.setLegends(['taylor'])
curve = ot.ParametricFunction(model, [0], [x0[1]]).getMarginal(
1).draw(a, b).getDrawable(0)
curve.setColor('red')
curve.setLegend('model')
graph.add(curve)
graph.setLegendPosition('topright')
view = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.143 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS