Greater¶
- class Greater(*args)¶
Greater comparison operator.
- Available constructors:
Greater()
See also
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> operator = ot.Greater() >>> print(operator(1, 2)) False >>> print(operator(2, 1)) True >>> print(operator(2, 2)) False
Methods
__call__(a, b)Call self as a function.
Accessor to the object's name.
getId()Accessor to the object's id.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
Accessor to the object's visibility state.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setShadowedId(id)Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
setVisibility(visible)Accessor to the object's visibility state.
- __init__(*args)¶
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getId()¶
Accessor to the object’s id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getShadowedId()¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getVisibility()¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Returns:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- hasVisibleName()¶
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
- Returns:
- hasVisibleNamebool
True if the name is not empty and not the default one.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setShadowedId(id)¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Parameters:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- setVisibility(visible)¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Parameters:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
Examples using the class¶
Use the Adaptive Directional Stratification Algorithm
Use the post-analytical importance sampling algorithm
Test the design point with the Strong Maximum Test
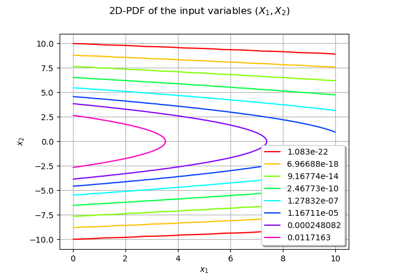
An illustrated example of a FORM probability estimate
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS