Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Estimate a process-based event probability¶
The objective of this example is to evaluate the probability of an event based on a stochastic process, using the Monte Carlo estimator.
Let be a stochastic process
of dimension
, where
is discretized on the mesh
.
We define the event as:
where is a domain of
.
We estimate the probabilty with the Monte Carlo
estimator.
The Monte Carlo algorithm is manipulated the same way as in the case where the event is based on a random variable independent of time.
We illustrate the algorithm on the example of the bidimensionnal white
noise process where
, distributed according to the bidimensionnal standard
normal distribution (with zero mean, unit variance and independent
marginals).
We consider the domain . Then the event
writes:
For all time stamps , the probability
that the process
enters into the domain
at time
writes, using the independence
property of the marginals:
with the cumulative distribution function of the scalar standard Normal distribution.
As the process is discretized on a time grid of size and using the
independence property of the white noise between two different time
stamps and the fact that the white noise follows the same distribution
at each time
, the final probability
writes:
With realizations, using the Monte Carlo estimator, we obtain
,
to be compared to the exact value
for a time grid of size
.
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
Create a time grid
tMin = 0.0
timeStep = 0.1
n = 100
tgrid = ot.RegularGrid(tMin, timeStep, n)
Create a normal process
amplitude = [5.0]
scale = [3.0]
model = ot.ExponentialModel(scale, amplitude)
process = ot.GaussianProcess(model, tgrid)
Create the 1-d domain A: [2.,5.]
lowerBound = [2.0]
upperBound = [5.0]
domain = ot.Interval(lowerBound, upperBound)
Create an event from a Process and a Domain
event = ot.ProcessEvent(process, domain)
Create the Monte-Carlo algorithm
montecarlo = ot.ProbabilitySimulationAlgorithm(event)
# Define the maximum number of simulations
montecarlo.setMaximumOuterSampling(1000)
# Define the block size
montecarlo.setBlockSize(100)
# Define the maximum coefficient of variation
montecarlo.setMaximumCoefficientOfVariation(0.0025)
# Run the algorithm
montecarlo.run()
# Get the result
montecarlo.getResult()
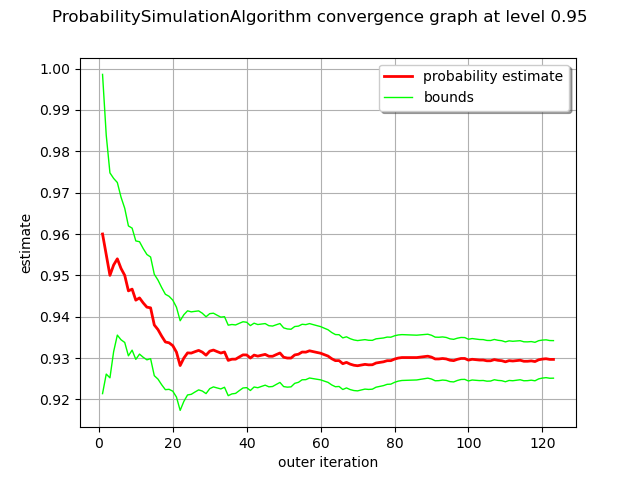
graph = montecarlo.drawProbabilityConvergence(0.95)
view = viewer.View(graph)
plt.show()
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS