Less¶
- class Less(*args)¶
Less comparison operator.
- Available constructors:
Less()
See also
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> operator = ot.Less() >>> print(operator(1, 2)) True >>> print(operator(2, 1)) False >>> print(operator(2, 2)) False
Methods
__call__(a, b)Call self as a function.
Accessor to the object's name.
getId()Accessor to the object's id.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
Accessor to the object's visibility state.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setShadowedId(id)Accessor to the object's shadowed id.
setVisibility(visible)Accessor to the object's visibility state.
- __init__(*args)¶
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getId()¶
Accessor to the object’s id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getShadowedId()¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getVisibility()¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Returns:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- hasVisibleName()¶
Test if the object has a distinguishable name.
- Returns:
- hasVisibleNamebool
True if the name is not empty and not the default one.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setShadowedId(id)¶
Accessor to the object’s shadowed id.
- Parameters:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- setVisibility(visible)¶
Accessor to the object’s visibility state.
- Parameters:
- visiblebool
Visibility flag.
Examples using the class¶
Estimate a probability with Latin Hypercube Sampling
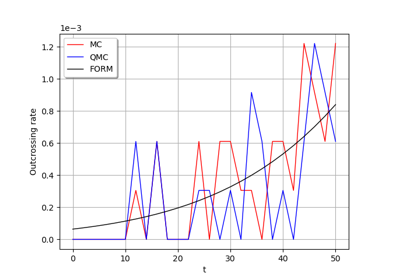
Estimate a probability with Monte-Carlo on axial stressed beam: a quick start guide to reliability
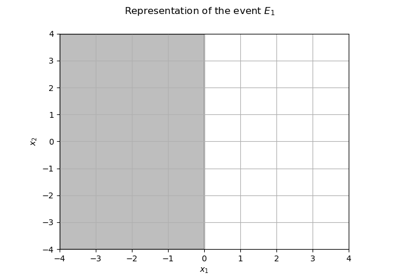
Use the FORM algorithm in case of several design points
Non parametric Adaptive Importance Sampling (NAIS)
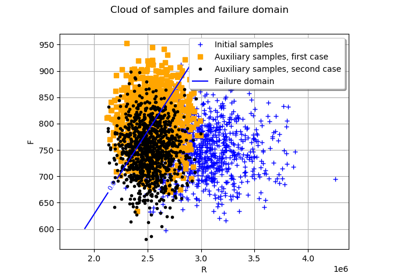
Axial stressed beam : comparing different methods to estimate a probability
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS