Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Introduction to OpenTURNS objects¶
In the otbenchmark package, we use several objects that must be known in order to distinguish which objects come from the OpenTURNS library or from otbenchmark. For reliability problems, there are three objects that cannot be ignored:
the
openturns.Function,
import openturns as ot
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import openturns.viewer as otv
Avoid mixture warnings
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
Distribution¶
Define two marginals
X0 = ot.Normal(0.0, 1.0)
X1 = ot.Uniform(0.0, 1.0)
Define an independent joint distribution
X_ind = ot.ComposedDistribution([X0, X1])
Define a dependent joint distribution using a copula (e.g., Frank copula)
copula = ot.FrankCopula(5)
X_dep = ot.ComposedDistribution([X0, X1], copula)
Generate a sample of each joint distribution
X_ind_sample = X_ind.getSample(1000)
X_dep_sample = X_dep.getSample(1000)
method_list = [method for method in dir(X0) if method.startswith("__") is False]
print(len(method_list))
151
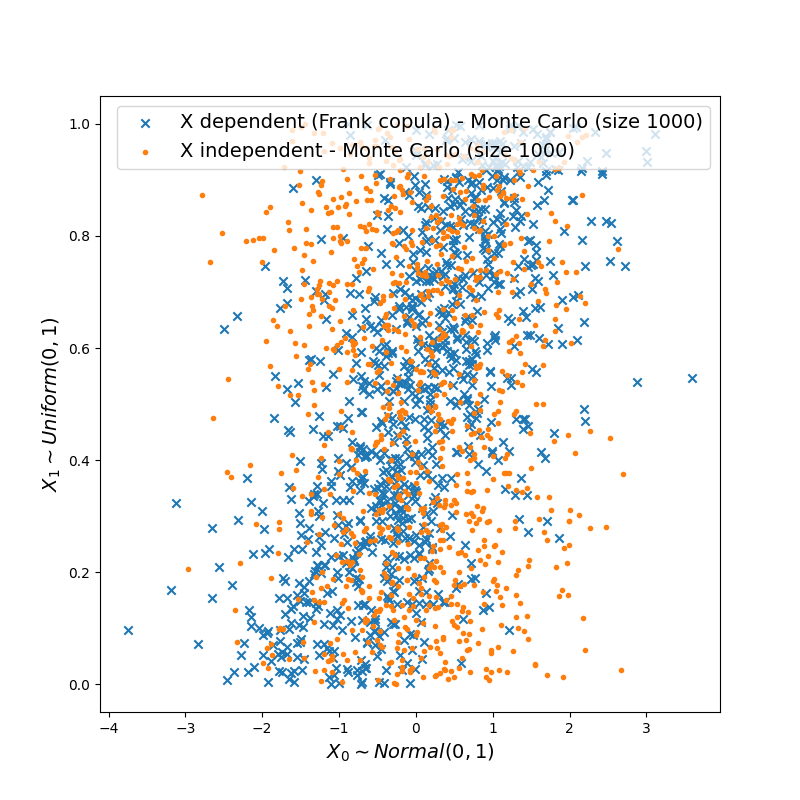
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.scatter(
X_dep_sample[:, 0],
X_dep_sample[:, 1],
label="X dependent (Frank copula) - Monte Carlo (size 1000)",
marker="x",
)
plt.scatter(
X_ind_sample[:, 0],
X_ind_sample[:, 1],
label="X independent - Monte Carlo (size 1000)",
marker=".",
)
plt.xlabel(r"$X_0 \sim Normal(0, 1)$", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel(r"$X_1 \sim Uniform(0, 1)$", fontsize=14)
_ = plt.legend(loc="best", fontsize=14)
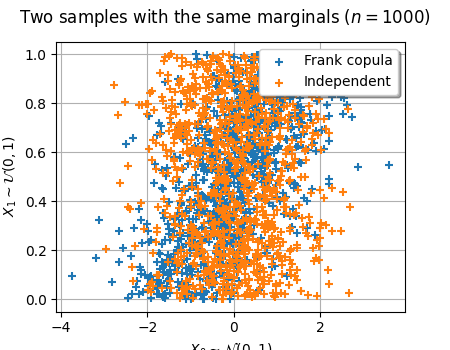
graph = ot.Graph(
"Two samples with the same marginals ($n=1000$)",
r"$X_0 \sim \mathcal{N}(0, 1)$",
r"$X_1 \sim \mathcal{U}(0, 1)$",
True,
)
cloud = ot.Cloud(X_dep_sample[:, 0], X_dep_sample[:, 1])
cloud.setLegend("Frank copula")
graph.add(cloud)
cloud = ot.Cloud(X_ind_sample[:, 0], X_ind_sample[:, 1])
cloud.setLegend("Independent")
graph.add(cloud)
graph.setLegendPosition("topright")
graph.setColors(ot.Drawable.BuildDefaultPalette(2))
view = otv.View(graph, figure_kw={"figsize": (4.5, 3.5)})
# view.save("two_samples.pdf")
Function¶
Define a symbolic function
myfunction = ot.SymbolicFunction(["x0", "x1"], ["sin(x0) * (1 + x1 ^ 2)"])
myfunction.setInputDescription(["$x_0$", "$x_1$"])
myfunction.setOutputDescription(["$y$"])
Define input random vectors
inputVect_ind = ot.RandomVector(X_ind)
inputVect_dep = ot.RandomVector(X_dep)
Compose input random vectors by the symbolic function
outputVect_ind = ot.CompositeRandomVector(myfunction, inputVect_ind)
outputVect_dep = ot.CompositeRandomVector(myfunction, inputVect_dep)
Sample the output random variable
outputSample_ind = outputVect_ind.getSample(10000)
outputSample_dep = outputVect_dep.getSample(10000)
plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6))
plt.hist(
outputSample_ind,
bins=40,
histtype="stepfilled",
alpha=0.3,
ec="k",
label="X independent",
)
plt.hist(
outputSample_dep,
bins=40,
histtype="stepfilled",
alpha=0.3,
ec="k",
label="X dependent (Frank copula)",
)
plt.xlabel("$g(X)$ histogram", fontsize=14)
_ = plt.legend(loc="best", fontsize=14)
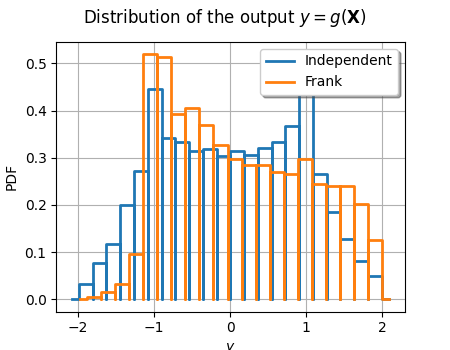
graph = ot.HistogramFactory().build(outputSample_ind).drawPDF()
graph.setLegends(["Independent"])
graph.setTitle(r"Distribution of the output $y=g(\mathbf{X})$")
curve = ot.HistogramFactory().build(outputSample_dep).drawPDF()
curve.setLegends(["Frank"])
graph.add(curve)
graph.setColors(ot.Drawable.BuildDefaultPalette(2))
view = otv.View(graph, figure_kw={"figsize": (4.5, 3.5)})
# view.save("histo_output.pdf")
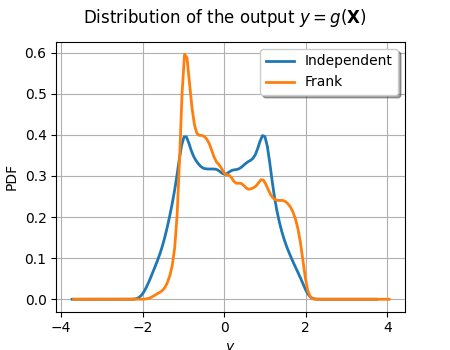
graph = ot.KernelSmoothing().build(outputSample_ind).drawPDF()
graph.setLegends(["Independent"])
graph.setTitle(r"Distribution of the output $y=g(\mathbf{X})$")
curve = ot.KernelSmoothing().build(outputSample_dep).drawPDF()
curve.setLegends(["Frank"])
graph.add(curve)
graph.setColors(ot.Drawable.BuildDefaultPalette(2))
view = otv.View(graph, figure_kw={"figsize": (4.5, 3.5)})
# view.save("kernel_output.pdf")
ThresholdEvent¶
threshold = 1.0 # Change this to 2.0 to turn it into a difficult problem
event = ot.ThresholdEvent(outputVect_ind, ot.Greater(), threshold)
event
maximumCoV = 0.05 # Coefficient of variation
maximumNumberOfBlocks = 100000
experiment = ot.MonteCarloExperiment()
algoMC = ot.ProbabilitySimulationAlgorithm(event, experiment)
algoMC.setMaximumOuterSampling(maximumNumberOfBlocks)
algoMC.setBlockSize(1)
algoMC.setMaximumCoefficientOfVariation(maximumCoV)
algoMC.run()
result = algoMC.getResult()
probability = result.getProbabilityEstimate()
print("Pf = ", probability)
Pf = 0.16262135922330098
otv.View.ShowAll()
Total running time of the script: (1 minutes 42.626 seconds)
 otbenchmark
otbenchmark