NLopt¶
- class NLopt(*args)¶
Interface to NLopt.
This class exposes the solvers from the non-linear optimization library [nlopt2009].
More details about available algorithms are available here.
- Parameters:
- problem
OptimizationProblem Optimization problem to solve.
- algoNamestr
The NLopt identifier of the algorithm. Use
GetAlgorithmNames()to list available names.
- problem
See also
AbdoRackwitz,Cobyla,SQP,TNC
Notes
Here are some properties of the different algorithms:
Algorithm
Derivative info
Constraint support
AUGLAG
no derivative
all
AUGLAG_EQ
no derivative
all
GD_MLSL
first derivative
bounds required
GD_MLSL_LDS
first derivative
bounds required
GD_STOGO (disabled)
first derivative
bounds required
GD_STOGO_RAND (disabled)
first derivative
bounds required
GN_AGS (disabled)
no derivative
bounds required, inequality
GN_CRS2_LM
no derivative
bounds required
GN_DIRECT
no derivative
bounds required
GN_DIRECT_L
no derivative
bounds required
GN_DIRECT_L_NOSCAL
no derivative
bounds required
GN_DIRECT_L_RAND
no derivative
bounds required
GN_DIRECT_L_RAND_NOSCAL
no derivative
bounds required
GN_ESCH
no derivative
bounds required
GN_ISRES
no derivative
bounds required, all
GN_MLSL
no derivative
bounds required
GN_MLSL_LDS
no derivative
bounds required
GN_ORIG_DIRECT
no derivative
bounds required, inequality
GN_ORIG_DIRECT_L
no derivative
bounds required, inequality
G_MLSL
no derivative
bounds required
G_MLSL_LDS
no derivative
bounds required
LD_AUGLAG
first derivative
all
LD_AUGLAG_EQ
first derivative
all
LD_CCSAQ
first derivative
bounds, inequality
LD_LBFGS
first derivative
bounds
LD_MMA
first derivative
bounds, inequality
LD_SLSQP
first derivative
all
LD_TNEWTON
first derivative
bounds
LD_TNEWTON_PRECOND
first derivative
bounds
LD_TNEWTON_PRECOND_RESTART
first derivative
bounds
LD_TNEWTON_RESTART
first derivative
bounds
LD_VAR1
first derivative
bounds
LD_VAR2
first derivative
bounds
LN_AUGLAG
no derivative
all
LN_AUGLAG_EQ
no derivative
all
LN_BOBYQA
no derivative
bounds
LN_COBYLA
no derivative
all
LN_NELDERMEAD
no derivative
bounds
LN_NEWUOA
no derivative
none
LN_NEWUOA_BOUND (disabled)
no derivative
bounds
LN_PRAXIS (disabled)
no derivative
bounds
LN_SBPLX
no derivative
bounds
Availability of algorithms marked as optional may vary depending on the NLopt version or compilation options used.
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> dim = 4 >>> bounds = ot.Interval([-3.0] * dim, [5.0] * dim) >>> linear = ot.SymbolicFunction(['x1', 'x2', 'x3', 'x4'], ['x1+2*x2-3*x3+4*x4']) >>> problem = ot.OptimizationProblem(linear, ot.Function(), ot.Function(), bounds) >>> print(ot.NLopt.GetAlgorithmNames()) [AUGLAG,AUGLAG_EQ,GD_MLSL,GD_MLSL_LDS,... >>> algo = ot.NLopt(problem, 'LD_MMA') >>> algo.setStartingPoint([0.0] * 4) >>> algo.run() >>> result = algo.getResult() >>> x_star = result.getOptimalPoint() >>> y_star = result.getOptimalValue()
Methods
Accessor to the list of algorithms provided by NLopt, by names.
Accessor to the algorithm name.
Accessor to check status flag.
Accessor to the object's name.
Initial local derivative-free algorithms step accessor.
Local solver accessor.
Accessor to maximum allowed absolute error.
Accessor to maximum allowed number of calls.
Accessor to maximum allowed constraint error.
Accessor to maximum allowed number of iterations.
Accessor to maximum allowed relative error.
Accessor to maximum allowed residual error.
Accessor to the maximum duration.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to optimization problem.
Accessor to optimization result.
getSeed()Random generator seed accessor.
Accessor to starting point.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
run()Launch the optimization.
setAlgorithmName(algoName)Accessor to the algorithm name.
setCheckStatus(checkStatus)Accessor to check status flag.
setInitialStep(initialStep)Initial local derivative-free algorithms step accessor.
setLocalSolver(localSolver)Local solver accessor.
setMaximumAbsoluteError(maximumAbsoluteError)Accessor to maximum allowed absolute error.
setMaximumCallsNumber(maximumCallsNumber)Accessor to maximum allowed number of calls
setMaximumConstraintError(maximumConstraintError)Accessor to maximum allowed constraint error.
setMaximumIterationNumber(maximumIterationNumber)Accessor to maximum allowed number of iterations.
setMaximumRelativeError(maximumRelativeError)Accessor to maximum allowed relative error.
setMaximumResidualError(maximumResidualError)Accessor to maximum allowed residual error.
setMaximumTimeDuration(maximumTime)Accessor to the maximum duration.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
setProblem(problem)Accessor to optimization problem.
setProgressCallback(*args)Set up a progress callback.
setResult(result)Accessor to optimization result.
setSeed(seed)Random generator seed accessor.
setStartingPoint(startingPoint)Accessor to starting point.
setStopCallback(*args)Set up a stop callback.
getMaximumEvaluationNumber
setMaximumEvaluationNumber
- __init__(*args)¶
- static GetAlgorithmNames()¶
Accessor to the list of algorithms provided by NLopt, by names.
- Returns:
- names
Description List of algorithm names provided by NLopt, according to its naming convention.
- names
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> print(ot.NLopt.GetAlgorithmNames()) [AUGLAG,AUGLAG_EQ,GD_MLSL,...
- getAlgorithmName()¶
Accessor to the algorithm name.
- Returns:
- algoNamestr
The NLopt identifier of the algorithm.
- getCheckStatus()¶
Accessor to check status flag.
- Returns:
- checkStatusbool
Whether to check the termination status. If set to False,
run()will not throw an exception if the algorithm does not fully converge and will allow one to still find a feasible candidate.
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getInitialStep()¶
Initial local derivative-free algorithms step accessor.
- Returns:
- dx
Point The initial step.
- dx
- getMaximumAbsoluteError()¶
Accessor to maximum allowed absolute error.
- Returns:
- maximumAbsoluteErrorfloat
Maximum allowed absolute error, where the absolute error is defined by
where
and
are two consecutive approximations of the optimum.
- getMaximumCallsNumber()¶
Accessor to maximum allowed number of calls.
- Returns:
- maximumEvaluationNumberint
Maximum allowed number of direct objective function calls through the () operator. Does not take into account eventual indirect calls through finite difference gradient calls.
- getMaximumConstraintError()¶
Accessor to maximum allowed constraint error.
- Returns:
- maximumConstraintErrorfloat
Maximum allowed constraint error, where the constraint error is defined by
where
is the current approximation of the optimum and
is the function that gathers all the equality and inequality constraints (violated values only)
- getMaximumIterationNumber()¶
Accessor to maximum allowed number of iterations.
- Returns:
- maximumIterationNumberint
Maximum allowed number of iterations.
- getMaximumRelativeError()¶
Accessor to maximum allowed relative error.
- Returns:
- maximumRelativeErrorfloat
Maximum allowed relative error, where the relative error is defined by
if
, else
.
- getMaximumResidualError()¶
Accessor to maximum allowed residual error.
- Returns:
- maximumResidualErrorfloat
Maximum allowed residual error, where the residual error is defined by
if
, else
.
- getMaximumTimeDuration()¶
Accessor to the maximum duration.
- Returns:
- maximumTimefloat
Maximum optimization duration in seconds.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- getProblem()¶
Accessor to optimization problem.
- Returns:
- problem
OptimizationProblem Optimization problem.
- problem
- getResult()¶
Accessor to optimization result.
- Returns:
- result
OptimizationResult Result class.
- result
- getSeed()¶
Random generator seed accessor.
- Returns:
- seedint
Seed.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- run()¶
Launch the optimization.
- setAlgorithmName(algoName)¶
Accessor to the algorithm name.
- Parameters:
- algoNamestr
The NLopt identifier of the algorithm.
- setCheckStatus(checkStatus)¶
Accessor to check status flag.
- Parameters:
- checkStatusbool
Whether to check the termination status. If set to False,
run()will not throw an exception if the algorithm does not fully converge and will allow one to still find a feasible candidate.
- setInitialStep(initialStep)¶
Initial local derivative-free algorithms step accessor.
- Parameters:
- dxsequence of float
The initial step.
- setMaximumAbsoluteError(maximumAbsoluteError)¶
Accessor to maximum allowed absolute error.
- Parameters:
- maximumAbsoluteErrorfloat
Maximum allowed absolute error, where the absolute error is defined by
where
and
are two consecutive approximations of the optimum.
- setMaximumCallsNumber(maximumCallsNumber)¶
Accessor to maximum allowed number of calls
- Parameters:
- maximumEvaluationNumberint
Maximum allowed number of direct objective function calls through the () operator. Does not take into account eventual indirect calls through finite difference gradient calls.
- setMaximumConstraintError(maximumConstraintError)¶
Accessor to maximum allowed constraint error.
- Parameters:
- maximumConstraintErrorfloat
Maximum allowed constraint error, where the constraint error is defined by
where
is the current approximation of the optimum and
is the function that gathers all the equality and inequality constraints (violated values only)
- setMaximumIterationNumber(maximumIterationNumber)¶
Accessor to maximum allowed number of iterations.
- Parameters:
- maximumIterationNumberint
Maximum allowed number of iterations.
- setMaximumRelativeError(maximumRelativeError)¶
Accessor to maximum allowed relative error.
- Parameters:
- maximumRelativeErrorfloat
Maximum allowed relative error, where the relative error is defined by
if
, else
.
- setMaximumResidualError(maximumResidualError)¶
Accessor to maximum allowed residual error.
- Parameters:
- maximumResidualErrorfloat
Maximum allowed residual error, where the residual error is defined by
if
, else
.
- setMaximumTimeDuration(maximumTime)¶
Accessor to the maximum duration.
- Parameters:
- maximumTimefloat
Maximum optimization duration in seconds.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setProblem(problem)¶
Accessor to optimization problem.
- Parameters:
- problem
OptimizationProblem Optimization problem.
- problem
- setProgressCallback(*args)¶
Set up a progress callback.
Can be used to programmatically report the progress of an optimization.
- Parameters:
- callbackcallable
Takes a float as argument as percentage of progress.
Examples
>>> import sys >>> import openturns as ot >>> rosenbrock = ot.SymbolicFunction(['x1', 'x2'], ['(1-x1)^2+100*(x2-x1^2)^2']) >>> problem = ot.OptimizationProblem(rosenbrock) >>> solver = ot.OptimizationAlgorithm(problem) >>> solver.setStartingPoint([0, 0]) >>> solver.setMaximumResidualError(1.e-3) >>> solver.setMaximumCallsNumber(10000) >>> def report_progress(progress): ... sys.stderr.write('-- progress=' + str(progress) + '%\n') >>> solver.setProgressCallback(report_progress) >>> solver.run()
- setResult(result)¶
Accessor to optimization result.
- Parameters:
- result
OptimizationResult Result class.
- result
- setSeed(seed)¶
Random generator seed accessor.
- Parameters:
- seedint
The RNG seed.
Notes
The default is set by the NLopt-InitialSeed ResourceMap entry.
- setStartingPoint(startingPoint)¶
Accessor to starting point.
- Parameters:
- startingPoint
Point Starting point.
- startingPoint
- setStopCallback(*args)¶
Set up a stop callback.
Can be used to programmatically stop an optimization.
- Parameters:
- callbackcallable
Returns an int deciding whether to stop or continue.
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> rosenbrock = ot.SymbolicFunction(['x1', 'x2'], ['(1-x1)^2+100*(x2-x1^2)^2']) >>> problem = ot.OptimizationProblem(rosenbrock) >>> solver = ot.OptimizationAlgorithm(problem) >>> solver.setStartingPoint([0, 0]) >>> solver.setMaximumResidualError(1.e-3) >>> solver.setMaximumCallsNumber(10000) >>> def ask_stop(): ... return True >>> solver.setStopCallback(ask_stop) >>> solver.run()
Examples using the class¶
Fitting a distribution with customized maximum likelihood
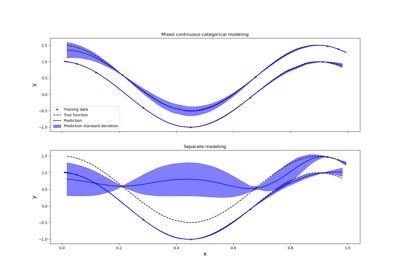
Kriging: metamodel with continuous and categorical variables
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS