PythonRandomVector¶
(Source code, png)
- class PythonRandomVector(dim=0)¶
Allow one to overload RandomVector from Python.
- Parameters:
- dimpositive int
Vector dimension. Default is 0.
See also
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0)
Overload RandomVector from Python:
>>> class RVEC(ot.PythonRandomVector): ... def __init__(self): ... super(RVEC, self).__init__(2) ... self.setDescription(['R', 'S']) ... ... def getRealization(self): ... X = [ot.RandomGenerator.Generate(), 2 + ot.RandomGenerator.Generate()] ... return X ... ... def getSample(self, size): ... X = [] ... for i in range(size): ... X.append([ot.RandomGenerator.Generate(), 2 + ot.RandomGenerator.Generate()]) ... return X ... ... def getMean(self): ... return [0.5, 2.5] ... ... def getCovariance(self): ... return [[0.0833333, 0.], [0., 0.0833333]]
Use the overloaded class:
>>> R = RVEC() >>> # Instance creation >>> myRV = ot.RandomVector(R) >>> # Realization >>> print(myRV.getRealization()) [0.629877,2.88281] >>> # Sample >>> print(myRV.getSample(5)) 0 : [ 0.135276 2.0325 ] 1 : [ 0.347057 2.96942 ] 2 : [ 0.92068 2.50304 ] 3 : [ 0.0632061 2.29276 ] 4 : [ 0.714382 2.38336 ] >>> # Mean >>> print(myRV.getMean()) [0.5,2.5] >>> # Covariance >>> print(myRV.getCovariance()) [[ 0.0833333 0 ] [ 0 0.0833333 ]]
Random vectors can admit parameters.
In the following example, we define a RandomVector to sample from a normal multivariate normal distribution truncated to a ball. We implement the setParameter method to define the ball’s center.
>>> class NormalTruncatedToBall(ot.PythonRandomVector): ... def __init__(self, dim, max_dist): ... super().__init__(dim) ... self._center = ot.Point(dim) ... self._normal = ot.Normal(dim) ... self._max_dist = max_dist ... self.setParameter(ot.Point(dim)) ... ... def getRealization(self): ... dist = ot.SpecFunc.MaxScalar ... while dist>self._max_dist: ... candidate = self._normal.getRealization() ... dist = (candidate - self._center).norm() ... return candidate ... ... def setParameter(self, center): # the parameter influences sampling ... self._center = center ... ... def getParameter(self): # implemented for the sake of consistency ... return self._center ... ... def getParameterDescription(self): # optional ... return ["center_{}".format(i) for i in range(self.getDimension())]
Define an instance of this RandomVector and set the parameter:
>>> myRV = ot.RandomVector(NormalTruncatedToBall(2, 1.5)) >>> myRV.setParameter([1.3, 0.6])
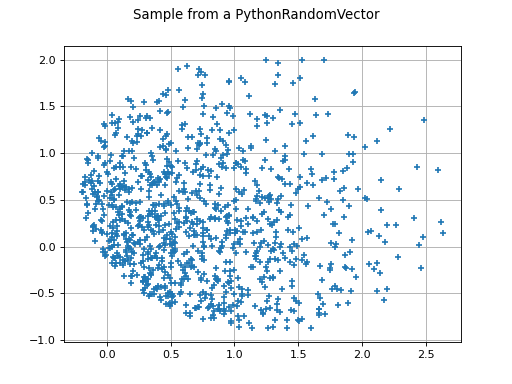
Get a sample and plot it:
>>> sample = myRV.getSample(100) >>> graph = ot.Graph("Sample from a PythonRandomVector", "", "", True, '') >>> cloud = ot.Cloud(sample) >>> graph.add(cloud) >>> from openturns.viewer import View >>> view = View(graph)
Methods
Get the description.
Get the dimension.
setDescription(desc)Set the description.
- __init__(dim=0)¶
- getDescription()¶
Get the description.
- Returns:
- desc
Description desc describes the components of the RandomVector.
- desc
- getDimension()¶
Get the dimension.
- Returns:
- dimpositive int
Dimension of the RandomVector.
- setDescription(desc)¶
Set the description.
- Parameters:
- descsequence of str
desc describes the components of the RandomVector. Its size must be equal to the dimension of the RandomVector.
Examples using the class¶
Linear Regression with interval-censored observations
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS