Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Compute Sobol’ indices confidence intervals¶
In this example we will estimate confidence intervals for chaos Sobol’ indices by bootstrap. Unlike estimation by sampling where the confidence intervals are obtained from the asymptotic distributions, there is currently no known analytical method to compute Sobol’ confidence intervals, so we can fallback to bootstrap.
Bootstraping the polynomial chaos is presented in [marelli2018] as “full bootstraping” and referred to as bootstrap-PCE or “bPCE”. Full bPCE can be CPU time consuming in some cases, e.g. when the dimension of the input random vector is large or when the training sample size is large. In the fast bPCE method, the sparse polynomial basis identified by the LARS algorithm is computed only once. Then bootstrapping is applied to the regression step on the sparse basis. Using fast bPCE is not straightforward, so we use full bPCE in the current example.
To do this, we must simultaneously bootstrap in the input and output samples, so that the
input/output mapping is preserved.
In the example below, we show how to use the BootstrapExperiment class for this purpose.
This involves the following steps:
Generate an initial input/output design of experiments ;
Compute a fixed number of bootstrap samples from the original design ;
For each input/output boostrap sample, compute Sobol’ indices by functional chaos ;
Compute quantiles of these Sobol’ indices realizations to get the confidence intervals.
import openturns as ot
from openturns.usecases import cantilever_beam
import openturns.viewer as otv
Load the cantilever beam use-case. We want to use the independent distribution to get meaningful Sobol’ indices.
beam = cantilever_beam.CantileverBeam()
g = beam.model
distribution = beam.independentDistribution
dim_input = distribution.getDimension()
Create the tensorized polynomial basis, with the default linear enumeration function.
marginals = [distribution.getMarginal(i) for i in range(dim_input)]
basis = ot.OrthogonalProductPolynomialFactory(marginals)
Generate a learning sample with Monte-Carlo simulations (or retrieve the design from experimental data).
ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0)
N = 35 # size of the experimental design
X = distribution.getSample(N)
Y = g(X)
def computeSparseLeastSquaresChaos(X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution):
"""
Create a sparse polynomial chaos with least squares.
* Uses the enumeration rule from basis.
* Uses LeastSquaresStrategy to compute the coefficients from
linear least squares.
* Uses LeastSquaresMetaModelSelectionFactory to select the polynomials
in the basis using least angle regression stepwise (LARS)
* Utilise LeastSquaresStrategy pour calculer les
coefficients par moindres carrés.
* Uses FixedStrategy to keep all coefficients that LARS has selected,
up to the given maximum total degree.
Parameters
----------
X : Sample(n)
The input training design of experiments with n points
Y : Sample(n)
The input training design of experiments with n points
basis : Basis
The multivariate orthogonal polynomial basis
total_degree : int
The maximum total polynomial degree
distribution : Distribution
The distribution of the input random vector
Returns
-------
result : FunctionalChaosResult
The polynomial chaos result
"""
selectionAlgorithm = ot.LeastSquaresMetaModelSelectionFactory()
projectionStrategy = ot.LeastSquaresStrategy(selectionAlgorithm)
enum_func = basis.getEnumerateFunction()
P = enum_func.getBasisSizeFromTotalDegree(total_degree)
adaptiveStrategy = ot.FixedStrategy(basis, P)
algo = ot.FunctionalChaosAlgorithm(
X, Y, distribution, adaptiveStrategy, projectionStrategy
)
algo.run()
result = algo.getResult()
return result
Build the chaos metamodel on the design of experiments.
total_degree = 3
result = computeSparseLeastSquaresChaos(X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution)
metamodel = result.getMetaModel()
Generate a validation sample independent of the training sample.
n_valid = 1000
X_test = distribution.getSample(n_valid)
Y_test = g(X_test)
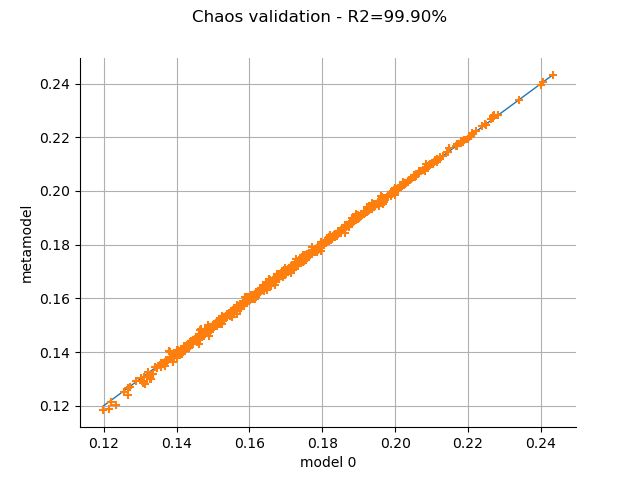
The MetaModelValidation class allows one to validate the metamodel on a test sample.
Plot the observed versus the predicted outputs.
metamodelPredictions = metamodel(X_test)
val = ot.MetaModelValidation(Y_test, metamodelPredictions)
graph = val.drawValidation()
r2Score = val.computeR2Score()[0]
graph.setTitle(f"Chaos validation - R2={r2Score * 100.0:.2f}%")
_ = otv.View(graph)
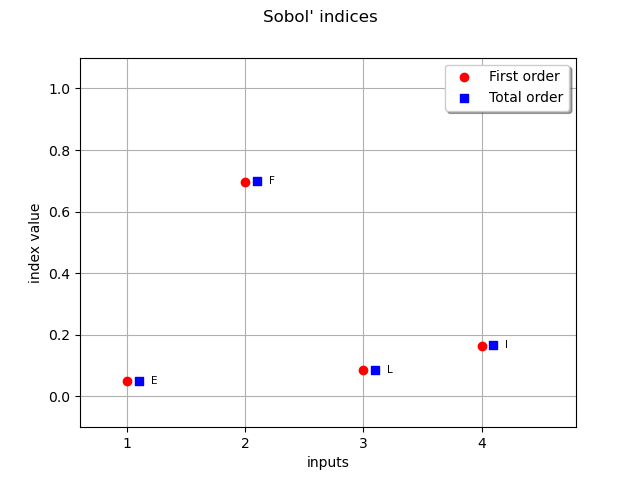
Retrieve Sobol’ sensitivity measures associated to the polynomial chaos decomposition of the model.
chaosSI = ot.FunctionalChaosSobolIndices(result)
fo_indices = [chaosSI.getSobolIndex(i) for i in range(dim_input)]
to_indices = [chaosSI.getSobolTotalIndex(i) for i in range(dim_input)]
input_names = g.getInputDescription()
graph = ot.SobolIndicesAlgorithm.DrawSobolIndices(input_names, fo_indices, to_indices)
_ = otv.View(graph)
We define the multiBootstrap function in order to simultaneously bootstrap in the input
and output samples, so that the input/output mapping is preserved.
We use the GenerateSelection method of the BootstrapExperiment class.
def multiBootstrap(*data):
"""
Bootstrap multiple samples at once.
Parameters
----------
data : sequence of Sample
Multiple samples to bootstrap.
Returns
-------
data_boot : sequence of Sample
The bootstrap samples.
"""
assert len(data) > 0, "empty list"
size = data[0].getSize()
selection = ot.BootstrapExperiment.GenerateSelection(size, size)
return [Z[selection] for Z in data]
Generate input/output bootstrap samples from the initial design.
X_boot, Y_boot = multiBootstrap(X, Y)
print(X_boot[:5])
print(Y_boot[:5])
[ E F L I ]
0 : [ 7.09376e+10 305.568 2.55637 1.34556e-07 ]
1 : [ 6.5963e+10 228.332 2.57804 1.53991e-07 ]
2 : [ 6.60008e+10 325.25 2.5146 1.45825e-07 ]
3 : [ 6.52443e+10 320.71 2.54539 1.40993e-07 ]
4 : [ 6.86026e+10 282.187 2.59881 1.42475e-07 ]
[ y0 ]
0 : [ 0.178271 ]
1 : [ 0.128386 ]
2 : [ 0.179111 ]
3 : [ 0.191651 ]
4 : [ 0.168912 ]
def computeChaosSensitivity(X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution):
"""
Compute the first and total order Sobol' indices from a polynomial chaos.
Parameters
----------
X, Y : Sample
Input/Output design
basis : Basis
Tensorized basis
total_degree : int
Maximal total degree
distribution : Distribution
Input distribution
Returns
-------
first_order, total_order: list of float
The first and total order indices.
"""
dim_input = X.getDimension()
result = computeSparseLeastSquaresChaos(X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution)
chaosSI = ot.FunctionalChaosSobolIndices(result)
first_order = [chaosSI.getSobolIndex(i) for i in range(dim_input)]
total_order = [chaosSI.getSobolTotalIndex(i) for i in range(dim_input)]
return first_order, total_order
def computeBootstrapChaosSobolIndices(
X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution, bootstrap_size
):
"""
Computes a bootstrap sample of first and total order indices from polynomial chaos.
Parameters
----------
X, Y : Sample
Input/Output design
basis : Basis
Tensorized basis
total_degree : int
Maximal total degree
distribution : Distribution
Input distribution
bootstrap_size : interval
The bootstrap sample size
"""
dim_input = X.getDimension()
fo_sample = ot.Sample(0, dim_input)
to_sample = ot.Sample(0, dim_input)
unit_eps = ot.Interval([1e-9] * dim_input, [1 - 1e-9] * dim_input)
for i in range(bootstrap_size):
X_boot, Y_boot = multiBootstrap(X, Y)
first_order, total_order = computeChaosSensitivity(
X_boot, Y_boot, basis, total_degree, distribution
)
if unit_eps.contains(first_order) and unit_eps.contains(total_order):
fo_sample.add(first_order)
to_sample.add(total_order)
return fo_sample, to_sample
Compute sample of Sobol’ indices by boostrap.
bootstrap_size = 500
fo_sample, to_sample = computeBootstrapChaosSobolIndices(
X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution, bootstrap_size
)
def computeSobolIndicesConfidenceInterval(fo_sample, to_sample, alpha=0.95):
"""
From a sample of first or total order indices,
compute a bilateral confidence interval of level alpha.
Estimates the distribution of the first and total order Sobol' indices
from a bootstrap estimation.
Then computes a bilateral confidence interval for each marginal.
Parameters
----------
fo_sample: ot.Sample(n, dim_input)
The first order indices
to_sample: ot.Sample(n, dim_input)
The total order indices
alpha : float
The confidence level
Returns
-------
fo_interval : ot.Interval
The confidence interval of first order Sobol' indices
to_interval : ot.Interval
The confidence interval of total order Sobol' indices
"""
dim_input = fo_sample.getDimension()
fo_lb = [0] * dim_input
fo_ub = [0] * dim_input
to_lb = [0] * dim_input
to_ub = [0] * dim_input
for i in range(dim_input):
fo_i = fo_sample[:, i]
to_i = to_sample[:, i]
beta = (1.0 - alpha) / 2
fo_lb[i] = fo_i.computeQuantile(beta)[0]
fo_ub[i] = fo_i.computeQuantile(1.0 - beta)[0]
to_lb[i] = to_i.computeQuantile(beta)[0]
to_ub[i] = to_i.computeQuantile(1.0 - beta)[0]
# Create intervals
fo_interval = ot.Interval(fo_lb, fo_ub)
to_interval = ot.Interval(to_lb, to_ub)
return fo_interval, to_interval
Compute confidence intervals from the indices samples.
fo_interval, to_interval = computeSobolIndicesConfidenceInterval(fo_sample, to_sample)
def computeAndDrawSobolIndices(
N, basis, total_degree, distribution, bootstrap_size=500, alpha=0.95
):
"""
Compute and draw Sobol' indices from a polynomial chaos based on a
given sample size.
Compute confidence intervals at level alpha from bootstrap.
"""
X = distribution.getSample(N)
Y = g(X)
fo_sample, to_sample = computeBootstrapChaosSobolIndices(
X, Y, basis, total_degree, distribution, bootstrap_size
)
fo_interval, to_interval = computeSobolIndicesConfidenceInterval(
fo_sample, to_sample, alpha
)
graph = ot.SobolIndicesAlgorithm.DrawSobolIndices(
input_names,
fo_sample.computeMean(),
to_sample.computeMean(),
fo_interval,
to_interval,
)
graph.setTitle(f"Sobol' indices - N={N}")
graph.setIntegerXTick(True)
return graph
Plot the boostrap Sobol’ indices mean and the confidence intervals. The confidence length will shrink if we increase the initial sample size.
sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 3
graph = computeAndDrawSobolIndices(30, basis, total_degree, distribution)
_ = otv.View(graph)
otv.View.ShowAll()
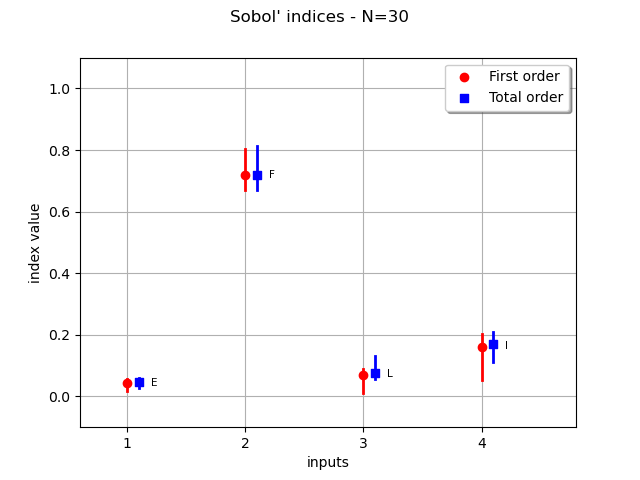
We see that the variable F has the highest sensitivity indices and that confidence intervals do not change this conclusion. The confidence intervals of the sensitivity indices of the variables L and I are similar so that we cannot say which of L or I is more significant than the other: both variables have similar sensitivity indices. The least sensitive variable is E, but the confidence intervals do not cross the X axis. Hence, there is no evidence that the Sobol’ indices of E are zero.
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.664 seconds)
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS