The Branin test case¶
Introduction¶
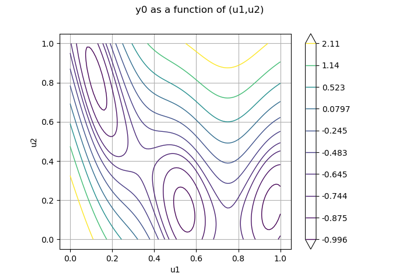
The Branin function is defined in 2 dimensions based on the functions :
and :
Finally, the Branin function is the composition of the two previous functions:
for any .
There are three global minimas:
and :
where the function value is:
We assume that the output of the Branin function is noisy, with a gaussian noise. In other words, the objective function is:
where is a Gaussian random variable with null mean and standard deviation
.
References¶
Dixon, L. C. W., & Szego, G. P. (1978). The global optimization problem: an introduction. Towards global optimization, 2, 1-15.
Forrester, A., Sobester, A., & Keane, A. (2008). Engineering design via surrogate modelling: a practical guide. Wiley.
Global Optimization Test Problems. Retrieved June 2013, from http://www-optima.amp.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp/member/student/hedar/Hedar_files/TestGO.htm.
Molga, M., & Smutnicki, C. Test functions for optimization needs (2005), from https://robertmarks.org/Classes/ENGR5358/Papers/functions.pdf.
Picheny, V., Wagner, T., & Ginsbourger, D. (2012). A benchmark of kriging-based infill criteria for noisy optimization.
API documentation¶
- class BraninModel
Data class for the Branin test function.
- Attributes:
- dimint
The dimension of the problem, dim=2.
- model
Function The Branin function
- trueNoiseFunctionfloat
Constant, small noise
.
- noiseModel
Function The noise function
- lowerbound
Pointin dimension dim. Default is 0.0 for each dimension.
- upperbound
Pointin dimension dim. Default is 1.0 for each dimension.
- xexact1
Point First minima location
.
- xexact2
Point Second minima location
.
- xexact3
Point Third minima location
.
- xexact
Sample All global minimas location gathered.
Examples
>>> from openturns.usecases import branin_function >>> # Load the Branin model >>> bm = branin_function.BraninModel()
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS