LogNormalFactory¶
(Source code, png)
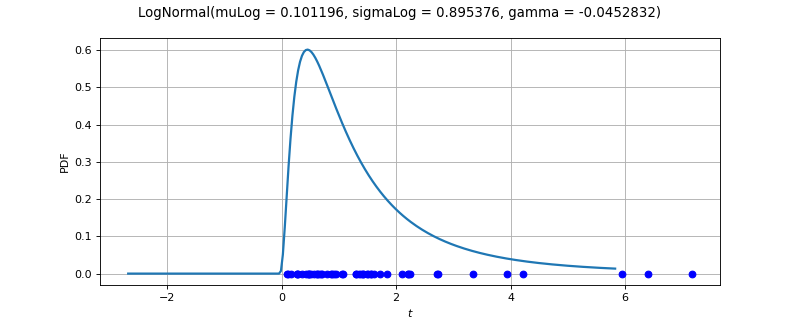
- class LogNormalFactory(*args)¶
Lognormal factory distribution.
Methods
build(*args)Build the distribution.
buildAsLogNormal(*args)Build the distribution as a LogNormal type.
buildEstimator(*args)Build the distribution and the parameter distribution.
buildMethodOfLeastSquares(sample)Build the distribution based on the least-squares estimator.
Build the distribution based on the local likelihood maximum estimator.
buildMethodOfModifiedMoments(sample)Build the distribution based on the modified moments estimator.
buildMethodOfMoments(sample)Build the distribution based on the method of moments estimator.
Accessor to the bootstrap size.
Accessor to the object's name.
Accessor to the known parameters indices.
Accessor to the known parameters values.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
setBootstrapSize(bootstrapSize)Accessor to the bootstrap size.
setKnownParameter(values, positions)Accessor to the known parameters.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
See also
Notes
Several estimators to build a LogNormal distribution from a scalar sample are proposed. The default strategy is using the local likelihood maximum estimator.
Moments based estimator:
Lets denote:
the empirical mean of the sample,
its empirical variance,
its empirical skewness.
We note
. The estimator
of
is the positive root of the relation:
(1)¶
Then we estimate
using:
(2)¶
where
.
Modified moments based estimator:
Using
and
previously defined, the third equation is:
(3)¶
The quantity
is the mean of the first order statistics of a standard normal sample of size
. We have:
(4)¶
where
and
are the PDF and CDF of the standard normal distribution. The estimator
of
is obtained as the solution of:
(5)¶
where
. Then we have
using the relations defined for the moments based estimator (2).
Local maximum likelihood estimator:
The following sums are defined:
The Maximum Likelihood estimator of
is defined by:
(6)¶
Thus,
satisfies the relation:
(7)¶
under the constraint
.
Least squares method estimator:
The parameter
is numerically optimized by non-linear least-squares:
where
are computed from linear least-squares at each optimization evaluation.
When
is known and the
follow a Log-Normal distribution then we use linear least-squares to solve the relation:
(8)¶
And the remaining parameters are estimated with:
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0) >>> sample = ot.LogNormal(1.5, 2.5, -1.5).getSample(1000) >>> estimated = ot.LogNormalFactory().build(sample)
- __init__(*args)¶
- build(*args)¶
Build the distribution.
Available usages:
build()
build(sample)
build(sample, method)
build(param)
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float, of dimension 1
The sample from which the distribution parameters are estimated.
- methodint
An integer corresponding to a specific estimator method:
0 : Local likelihood maximum estimator
1 : Modified moment estimator
2 : Method of moment estimator
3 : Least squares method.
The default value is 0. It is stored in
ResourceMap, key LogNormalFactory-EstimationMethod.- paramCollection of
PointWithDescription A vector of parameters of the distribution.
- Returns:
- dist
Distribution The built distribution.
- dist
Notes
See the
buildAsLogNormal()method.
- buildAsLogNormal(*args)¶
Build the distribution as a LogNormal type.
Available usages:
buildAsLogNormal()
buildAsLogNormal(sample)
buildAsLogNormal(sample, method)
buildAsLogNormal(param)
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float, of dimension 1
The sample from which the distribution parameters are estimated.
- methodint
An integer ranges from 0 to 2 corresponding to a specific estimator method:
0 : Local likelihood maximum estimator
1 : Modified moment estimator
2 : Method of moment estimator
3 : Least squares method.
Default value is 0. It is stored in
ResourceMap, key LogNormalFactory-EstimationMethod.- paramCollection of
PointWithDescription A vector of parameters of the distribution.
- Returns:
- dist
LogNormal The estimated distribution as a LogNormal.
- dist
Notes
In the first usage, the default
LogNormaldistribution is built.In the second usage, the parameters are evaluated according the following strategy:
It first uses the local likelihood maximum based estimator.
It uses the modified moments based estimator if the resolution of (7) is not possible.
It uses the moments based estimator, which are always defined, if the resolution of (5) is not possible.
In the third usage, the parameters of the
LogNormalare estimated using the given method.In the fourth usage, a
LogNormaldistribution corresponding to the given parameters is built.
- buildEstimator(*args)¶
Build the distribution and the parameter distribution.
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float
Data.
- parameters
DistributionParameters Optional, the parametrization.
- Returns:
- resDist
DistributionFactoryResult The results.
- resDist
Notes
According to the way the native parameters of the distribution are estimated, the parameters distribution differs:
Moments method: the asymptotic parameters distribution is normal and estimated by Bootstrap on the initial data;
Maximum likelihood method with a regular model: the asymptotic parameters distribution is normal and its covariance matrix is the inverse Fisher information matrix;
Other methods: the asymptotic parameters distribution is estimated by Bootstrap on the initial data and kernel fitting (see
KernelSmoothing).
If another set of parameters is specified, the native parameters distribution is first estimated and the new distribution is determined from it:
if the native parameters distribution is normal and the transformation regular at the estimated parameters values: the asymptotic parameters distribution is normal and its covariance matrix determined from the inverse Fisher information matrix of the native parameters and the transformation;
in the other cases, the asymptotic parameters distribution is estimated by Bootstrap on the initial data and kernel fitting.
- buildMethodOfLeastSquares(sample)¶
Build the distribution based on the least-squares estimator.
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float, of dimension 1
The sample from which the distribution parameters are estimated.
- gammafloat, optional
The
parameter estimate
- Returns:
- dist
LogNormal The built distribution.
- dist
- buildMethodOfLocalLikelihoodMaximization(sample)¶
Build the distribution based on the local likelihood maximum estimator.
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float, of dimension 1
The sample from which the distribution parameters are estimated.
- Returns:
- dist
LogNormal The built distribution.
- dist
- buildMethodOfModifiedMoments(sample)¶
Build the distribution based on the modified moments estimator.
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float, of dimension 1
The sample from which the distribution parameters are estimated.
- Returns:
- dist
LogNormal The built distribution.
- dist
- buildMethodOfMoments(sample)¶
Build the distribution based on the method of moments estimator.
- Parameters:
- sample2-d sequence of float, of dimension 1
The sample from which the distribution parameters are estimated.
- Returns:
- dist
LogNormal The built distribution.
- dist
- getBootstrapSize()¶
Accessor to the bootstrap size.
- Returns:
- sizeint
Size of the bootstrap.
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getKnownParameterIndices()¶
Accessor to the known parameters indices.
- Returns:
- indices
Indices Indices of the known parameters.
- indices
- getKnownParameterValues()¶
Accessor to the known parameters values.
- Returns:
- values
Point Values of known parameters.
- values
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- setBootstrapSize(bootstrapSize)¶
Accessor to the bootstrap size.
- Parameters:
- sizeint
The size of the bootstrap.
- setKnownParameter(values, positions)¶
Accessor to the known parameters.
- Parameters:
- valuessequence of float
Values of known parameters.
- positionssequence of int
Indices of known parameters.
Examples
When a subset of the parameter vector is known, the other parameters only have to be estimated from data.
In the following example, we consider a sample and want to fit a
Betadistribution. We assume that theand
parameters are known beforehand. In this case, we set the third parameter (at index 2) to -1 and the fourth parameter (at index 3) to 1.
>>> import openturns as ot >>> ot.RandomGenerator.SetSeed(0) >>> distribution = ot.Beta(2.3, 2.2, -1.0, 1.0) >>> sample = distribution.getSample(10) >>> factory = ot.BetaFactory() >>> # set (a,b) out of (r, t, a, b) >>> factory.setKnownParameter([-1.0, 1.0], [2, 3]) >>> inf_distribution = factory.build(sample)
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
Examples using the class¶
Fitting a distribution with customized maximum likelihood
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS