Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Example 2: Morris use-case and LHS initial design¶
To define the trajectories, we first get an LHS design in the box of size
We set the number of trajectories input variables are randomly to 10.
import openturns as ot
import otmorris
import openturns.viewer as otv
use the reference 20-d function from the Morris paper
f = ot.Function(otmorris.MorrisFunction())
dim = f.getInputDimension()
Number of trajectories
r = 10
Define an LHS experiment of size 50 in [0, 1]^20
size = 50
dist = ot.ComposedDistribution([ot.Uniform(0, 1)] * dim)
lhs_experiment = ot.LHSExperiment(dist, size, True, False)
lhsDesign = lhs_experiment.generate()
morris_experiment = otmorris.MorrisExperimentLHS(lhsDesign, r)
bounds = ot.Interval(dim) # [0, 1]^20
X = morris_experiment.generate()
Y = f(X)
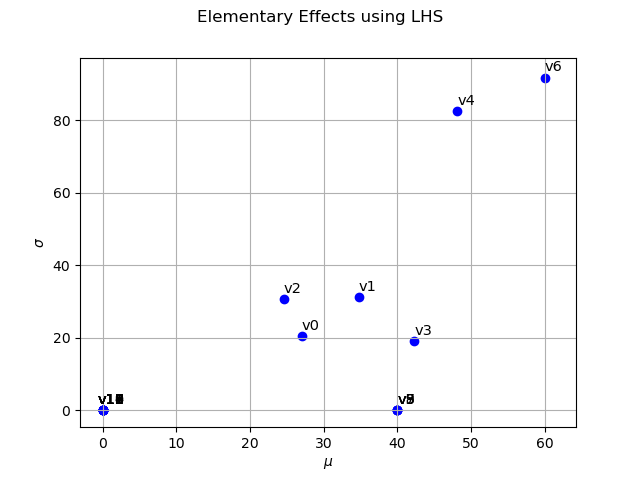
Evaluate Elementary effects (ee)
morris = otmorris.Morris(X, Y, bounds)
Compute mu/sigma
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.712 seconds)