Greater¶
- class Greater(*args)¶
Greater comparison operator.
See also
Examples
>>> import openturns as ot >>> operator = ot.Greater() >>> print(operator(1, 2)) False >>> print(operator(2, 1)) True >>> print(operator(2, 2)) False
Methods
Accessor to the object's name.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
hasName()Test if the object is named.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
- __init__(*args)¶
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- hasName()¶
Test if the object is named.
- Returns:
- hasNamebool
True if the name is not empty.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
Examples using the class¶
Use the Adaptive Directional Stratification Algorithm
Use the Adaptive Directional Stratification Algorithm
Use the post-analytical importance sampling algorithm
Use the post-analytical importance sampling algorithm
Test the design point with the Strong Maximum Test
Test the design point with the Strong Maximum Test
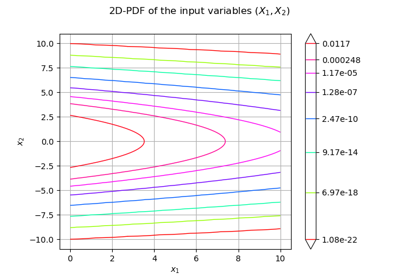
An illustrated example of a FORM probability estimate
An illustrated example of a FORM probability estimate
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS