Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Use the FORM - SORM algorithms¶
In this example we estimate a failure probability with the FORM algorithm on the cantilever beam example. More precisely, we show how to use the associated results:
the design point in both physical and standard space,
the probability estimation according to the FORM approximation, and the following SORM ones: Tvedt, Hohenbichler and Breitung,
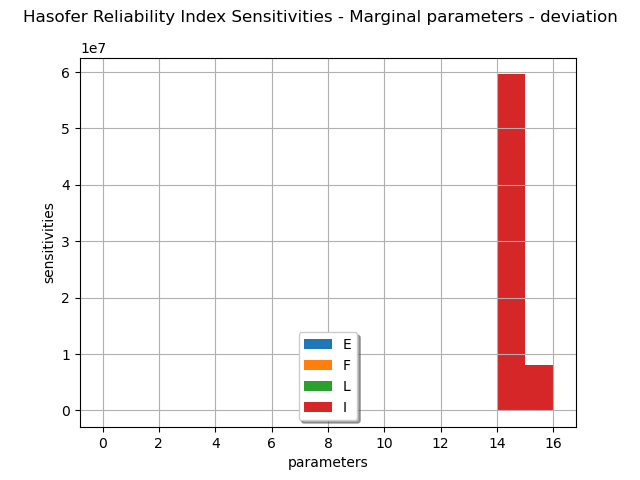
the Hasofer reliability index and the generalized ones evaluated from the Breitung, Tvedt and Hohenbichler approximations,
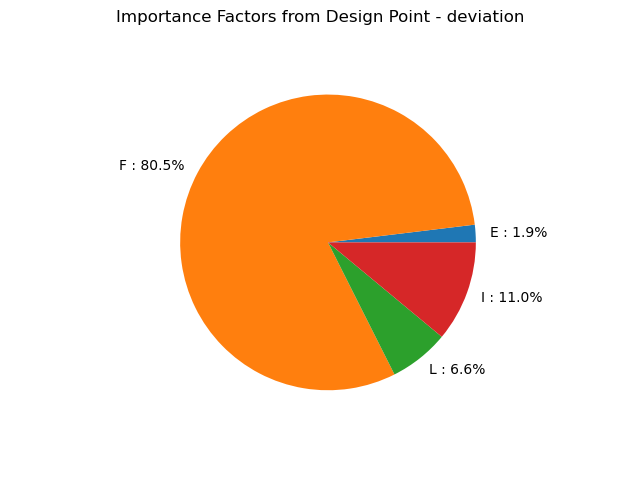
the importance factors defined as the normalized director factors of the design point in the
-space
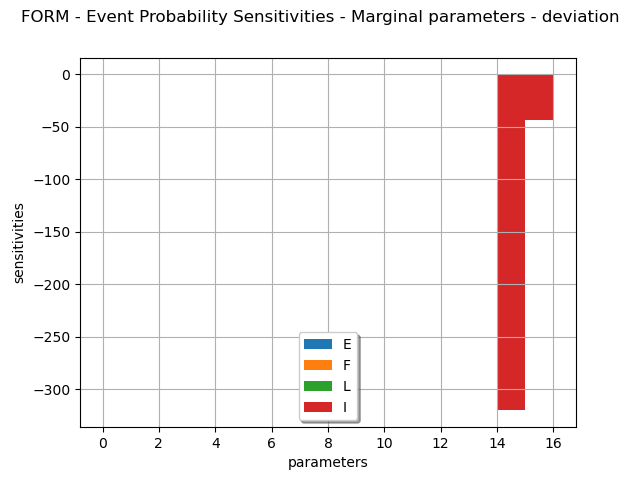
the sensitivity factors of the Hasofer reliability index and the FORM probability.
the coordinates of the mean point in the standard event space.
The coordinates of the mean point in the standard event space is:
where is the spheric univariate distribution of the standard space and
is the reliability index.
Model definition¶
from openturns.usecases import cantilever_beam
import openturns as ot
import openturns.viewer as viewer
from matplotlib import pylab as plt
ot.Log.Show(ot.Log.NONE)
We load the model from the usecases module :
cb = cantilever_beam.CantileverBeam()
We use the input parameters distribution from the data class :
distribution = cb.distribution
distribution.setDescription(["E", "F", "L", "I"])
We define the model
model = cb.model
Create the event whose probability we want to estimate.
vect = ot.RandomVector(distribution)
G = ot.CompositeRandomVector(model, vect)
event = ot.ThresholdEvent(G, ot.Greater(), 0.3)
event.setName("deviation")
FORM Analysis¶
Define a solver
optimAlgo = ot.Cobyla()
optimAlgo.setMaximumEvaluationNumber(1000)
optimAlgo.setMaximumAbsoluteError(1.0e-10)
optimAlgo.setMaximumRelativeError(1.0e-10)
optimAlgo.setMaximumResidualError(1.0e-10)
optimAlgo.setMaximumConstraintError(1.0e-10)
Run FORM
algo = ot.FORM(optimAlgo, event, distribution.getMean())
algo.run()
result = algo.getResult()
Analysis of the results¶
Probability
result.getEventProbability()
1.0900370418627377e-06
Hasofer reliability index
result.getHasoferReliabilityIndex()
4.735972259888528
Design point in the standard U* space.
print(result.getStandardSpaceDesignPoint())
[-0.665643,4.31264,1.23029,-1.3689]
Design point in the physical X space.
print(result.getPhysicalSpaceDesignPoint())
[6.56566e+10,458.976,2.58907,1.34803e-07]
Importance factors
graph = result.drawImportanceFactors()
view = viewer.View(graph)
marginalSensitivity, otherSensitivity = result.drawHasoferReliabilityIndexSensitivity()
marginalSensitivity.setLegends(["E", "F", "L", "I"])
marginalSensitivity.setLegendPosition("bottom")
view = viewer.View(marginalSensitivity)
marginalSensitivity, otherSensitivity = result.drawEventProbabilitySensitivity()
marginalSensitivity.setLegends(["E", "F", "L", "I"])
marginalSensitivity.setLegendPosition("bottom")
view = viewer.View(marginalSensitivity)
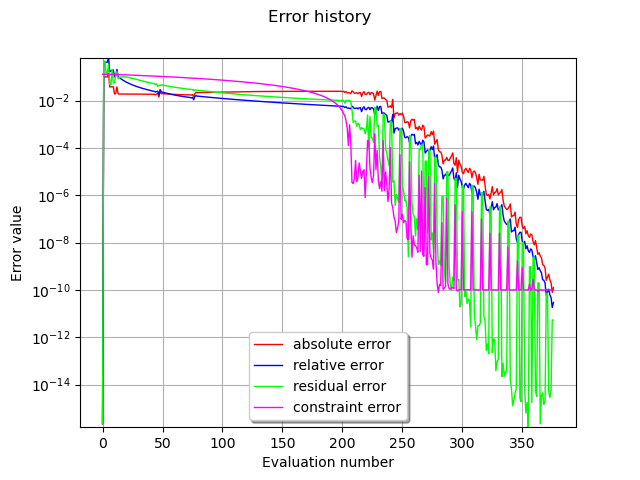
Error history
optimResult = result.getOptimizationResult()
graphErrors = optimResult.drawErrorHistory()
graphErrors.setLegendPosition("bottom")
graphErrors.setYMargin(0.0)
view = viewer.View(graphErrors)
Get additional results with SORM
algo = ot.SORM(optimAlgo, event, distribution.getMean())
algo.run()
sorm_result = algo.getResult()
Reliability index with Breitung approximation
sorm_result.getGeneralisedReliabilityIndexBreitung()
4.915018845541476
… with Hohenbichler approximation
sorm_result.getGeneralisedReliabilityIndexHohenbichler()
4.920394497861181
sorm_result.getGeneralisedReliabilityIndexTvedt()
4.923707817325712
SORM probability of the event with Breitung approximation
sorm_result.getEventProbabilityBreitung()
4.4386959812405013e-07
… with Hohenbichler approximation
sorm_result.getEventProbabilityHohenbichler()
4.318497365409196e-07
… with Tvedt approximation
sorm_result.getEventProbabilityTvedt()
plt.show()
FORM analysis with finite difference gradient¶
When the considered function has no analytical expression, the gradient may not be known. In this case, a constant step finite difference gradient definition may be used.
def cantilever_beam_python(X):
E, F, L, II = X
return [F * L ** 3 / (3 * E * II)]
cbPythonFunction = ot.PythonFunction(4, 1, func=cantilever_beam_python)
epsilon = [1e-8] * 4 # Here, a constant step of 1e-8 is used for every dimension
gradStep = ot.ConstantStep(epsilon)
cbPythonFunction.setGradient(
ot.CenteredFiniteDifferenceGradient(gradStep, cbPythonFunction.getEvaluation())
)
G = ot.CompositeRandomVector(cbPythonFunction, vect)
event = ot.ThresholdEvent(G, ot.Greater(), 0.3)
event.setName("deviation")
However, given the different nature of the model variables, a blended (variable) finite difference step may be preferable: The step depends on the location in the input space
gradStep = ot.BlendedStep(epsilon)
cbPythonFunction.setGradient(
ot.CenteredFiniteDifferenceGradient(gradStep, cbPythonFunction.getEvaluation())
)
G = ot.CompositeRandomVector(cbPythonFunction, vect)
event = ot.ThresholdEvent(G, ot.Greater(), 0.3)
event.setName("deviation")
We can then run the FORM analysis in the same way as before:
algo = ot.FORM(optimAlgo, event, distribution.getMean())
algo.run()
result = algo.getResult()
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS