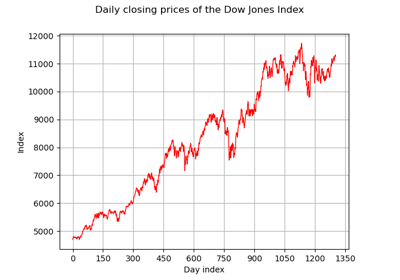
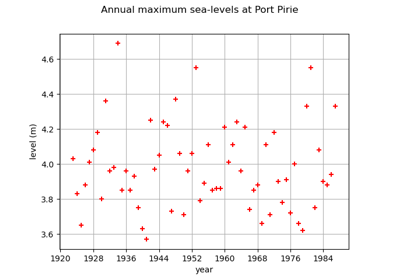
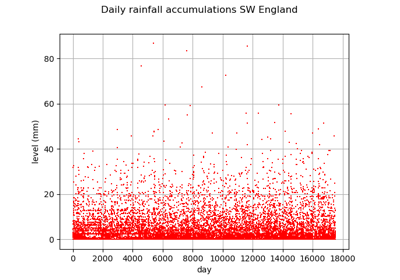
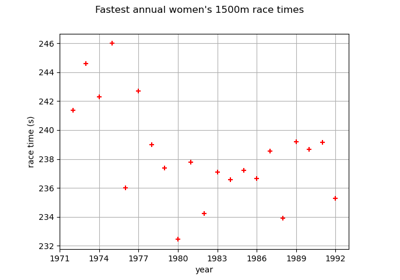
InterfaceObject¶
- class InterfaceObject(*args, **kwargs)¶
Methods
Accessor to the object's name.
getId()Accessor to the object's id.
getName()Accessor to the object's name.
setName(name)Accessor to the object's name.
- __init__(*args, **kwargs)¶
- getClassName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- class_namestr
The object class name (object.__class__.__name__).
- getId()¶
Accessor to the object’s id.
- Returns:
- idint
Internal unique identifier.
- getName()¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Returns:
- namestr
The name of the object.
- setName(name)¶
Accessor to the object’s name.
- Parameters:
- namestr
The name of the object.
Examples using the class¶
A quick start guide to the Point and Sample classes
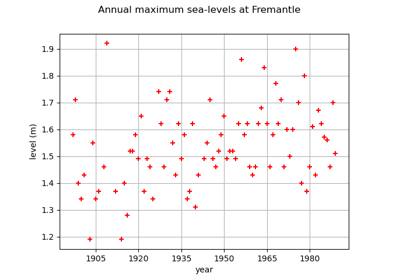
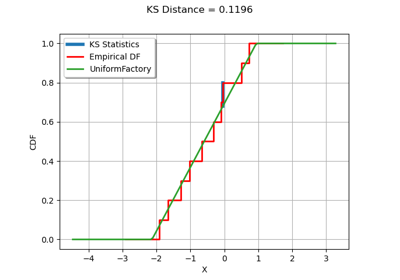
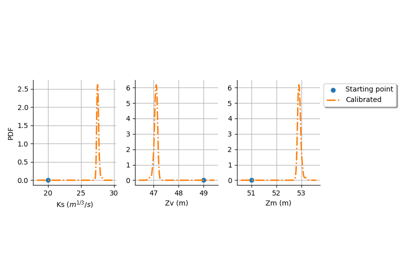
Kolmogorov-Smirnov : get the statistics distribution
Estimate tail dependence coefficients on the wave-surge data
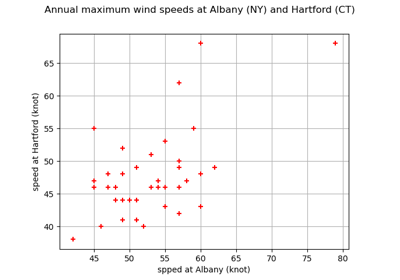
Estimate tail dependence coefficients on the wind data
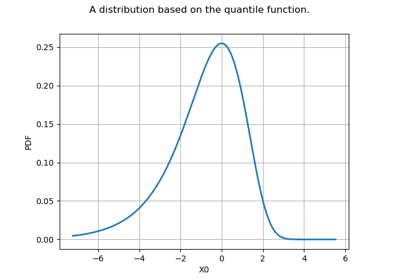
Create your own distribution given its quantile function
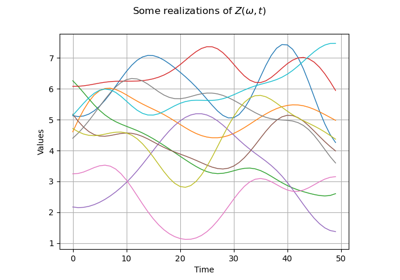
Create a process from random vectors and processes
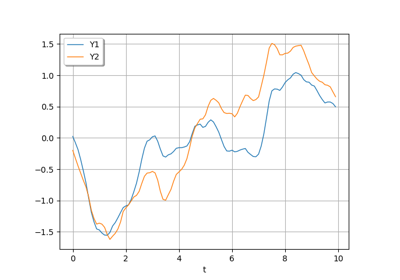
Sample trajectories from a Gaussian Process with correlated outputs
Apply a transform or inverse transform on your polynomial chaos
Create a full or sparse polynomial chaos expansion
Create a polynomial chaos metamodel from a data set
Conditional expectation of a polynomial chaos expansion
Example of multi output Kriging on the fire satellite model
Kriging: metamodel with continuous and categorical variables
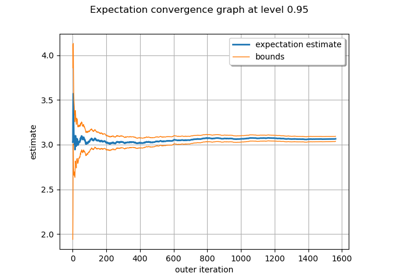
Evaluate the mean of a random vector by simulations
Use the Adaptive Directional Stratification Algorithm
Use the post-analytical importance sampling algorithm
Estimate a probability with Monte-Carlo on axial stressed beam: a quick start guide to reliability
Use the FORM algorithm in case of several design points
Non parametric Adaptive Importance Sampling (NAIS)
Test the design point with the Strong Maximum Test
Axial stressed beam : comparing different methods to estimate a probability
An illustrated example of a FORM probability estimate
Using the FORM - SORM algorithms on a nonlinear function
Estimate Sobol indices on a field to point function
Estimate Sobol’ indices for a function with multivariate output
Example of sensitivity analyses on the wing weight model
Create mixed deterministic and probabilistic designs of experiments
Create a design of experiments with discrete and continuous variables
Defining Python and symbolic functions: a quick start introduction to functions
Create a multivariate basis of functions from scalar multivariable functions
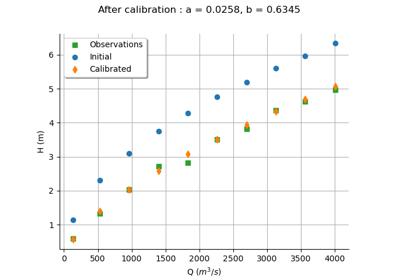
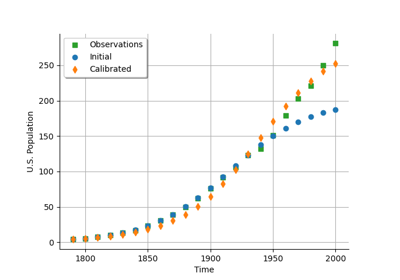
Calibrate a parametric model: a quick-start guide to calibration
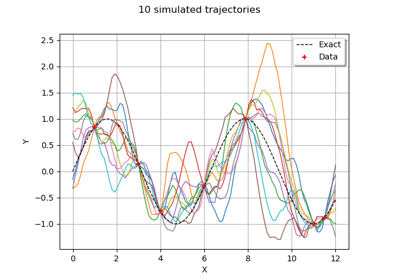
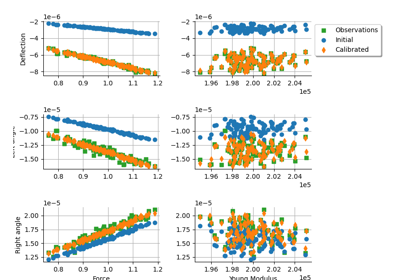
Generate observations of the Chaboche mechanical model
Linear Regression with interval-censored observations
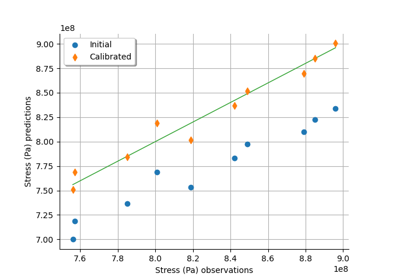
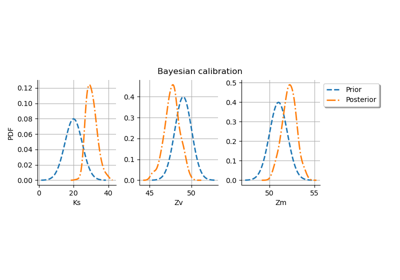
Bayesian calibration of hierarchical fission gas release models
Estimate a multivariate integral with IteratedQuadrature
Compute leave-one-out error of a polynomial chaos expansion
Compute confidence intervals of a regression model from data
Compute confidence intervals of a univariate noisy function
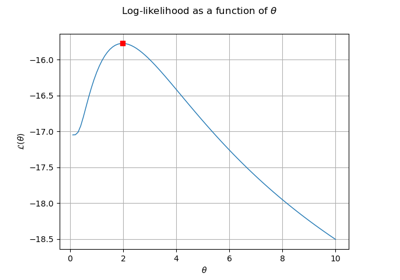
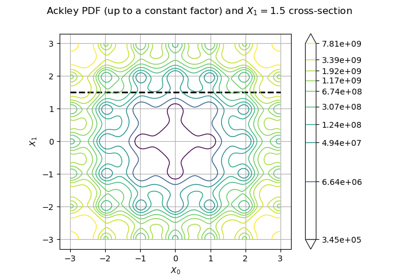
Plot the log-likelihood contours of a distribution
 OpenTURNS
OpenTURNS